Xanthan Gum Powder Food Grade Fufeng Xanthan Gum 200 Mesh CAS 11138-66-2

Product Description:
Xanthan gum, also known as xanthanic acid, is a polymer polysaccharide that is widely used in food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and other industries for its excellent gel properties and stability.
Here is a brief introduction to some of the physical and chemical properties of xanthan gum:
Appearance and solubility: Xanthan gum is a white to off-white powdery substance. It has excellent solubility in water and forms viscous solutions.
Gel properties: Xanthan gum can form a stable gel structure under appropriate concentration and pH conditions. The xanthan gum gel after gel formation has viscosity, elasticity and stability, which can increase the viscosity of the product, improve the texture, and stabilize emulsions and suspensions.
pH stability: Xanthan gum exhibits good stability within the conventional pH range (pH 2-12) and is not prone to degradation or gel failure.
Temperature stability: Xanthan gum shows good stability within a certain temperature range. Generally, the performance of xanthan gum will not be significantly affected in the range of 50-100 degrees Celsius.
Oxidation: Xanthan gum has excellent oxidation stability and is not prone to oxidation reactions and free radical damage.
Interaction between heavy metal ions and xanthan gum: Xanthan gum can undergo complex reactions with a variety of ions. Specifically, metal ions such as ammonium ions, calcium ions, and lithium ions can interact with xanthan gum and affect its performance and stability.
Salt tolerance: Xanthan gum can withstand higher concentration of salt solutions and is not prone to gel failure or precipitation.
Overall, xanthan gum has good stability, gelling and solubility and can play an important role in different fields. Its physical and chemical properties make xanthan gum an important ingredient in many products such as juices, gel foods, lotions, pharmaceutical capsules, eye drops, cosmetics, etc.
How does Xanthan Gum work?
Xanthan gum is used as a thickener and stabilizer in a variety of foods, drugs, and cosmetics. It results from the fermentation of carbohydrates by a specific strain of bacteria called Xanthomonas campestris. Xanthan gum’s mechanism of action involves its unique molecular structure. It consists of long chains of sugar molecules (mainly glucose) connected to each other through the side chains of other sugars. This structure enables it to interact with water and form a viscous solution or gel.
When xanthan gum is dispersed in a liquid, it hydrates and forms a network of long, tangled chains. This network acts as a thickener, increasing the viscosity of the liquid. The thickness or viscosity depends on the concentration of xanthan gum used. The thickening effect of xanthan gum is due to its ability to retain water and prevent it from separating. It forms a stable gel structure that traps water molecules, creating a thick, creamy texture in the liquid. This property is particularly useful in applications that require ideal texture and mouthfeel, such as sauces, dressings and dairy products.
In addition to its thickening effect, xanthan gum also has a stabilizing effect. It helps maintain product uniformity and homogeneity by preventing ingredients from settling or separating. It stabilizes emulsions, suspensions and foams, ensuring long-term product stability. Additionally, xanthan gum exhibits pseudoplastic behavior, meaning it thins when subjected to shear forces such as stirring or pumping. This property allows the product to dispense or flow easily while maintaining the desired consistency when at rest. Overall, the role of xanthan gum is to form a three-dimensional matrix in solution that thickens, stabilizes and provides desired textural properties to a variety of products.
Kosher Statement:
We hereby confirm that this product has been certified to Kosher standards.


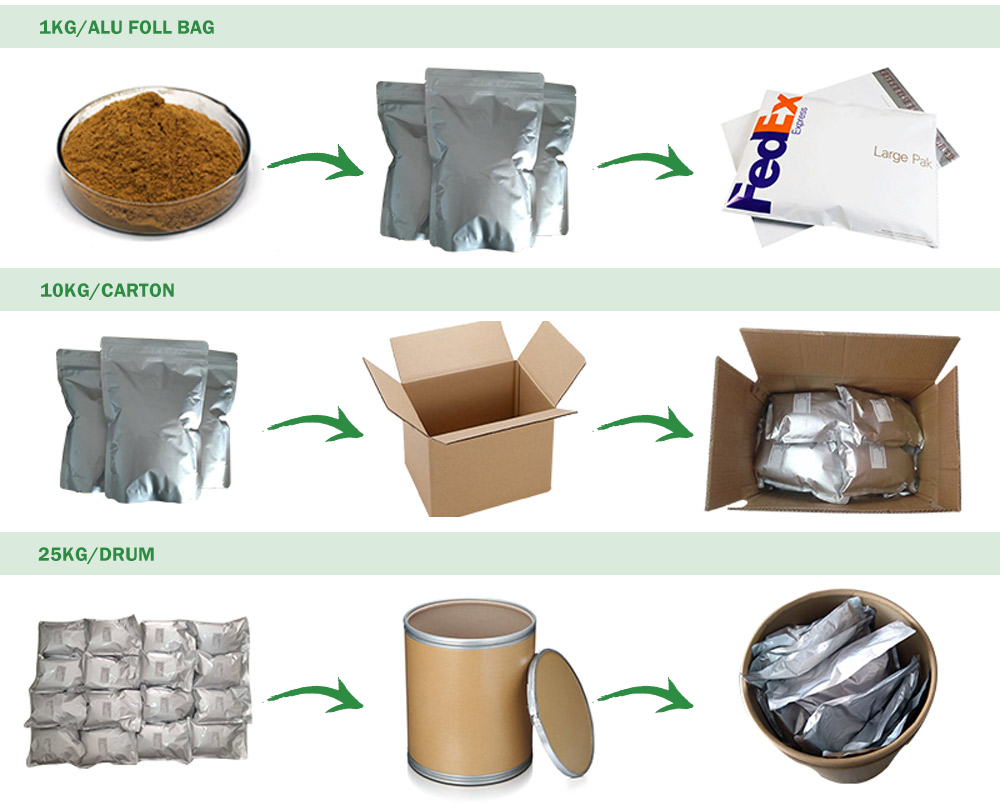
package & delivery


transportation