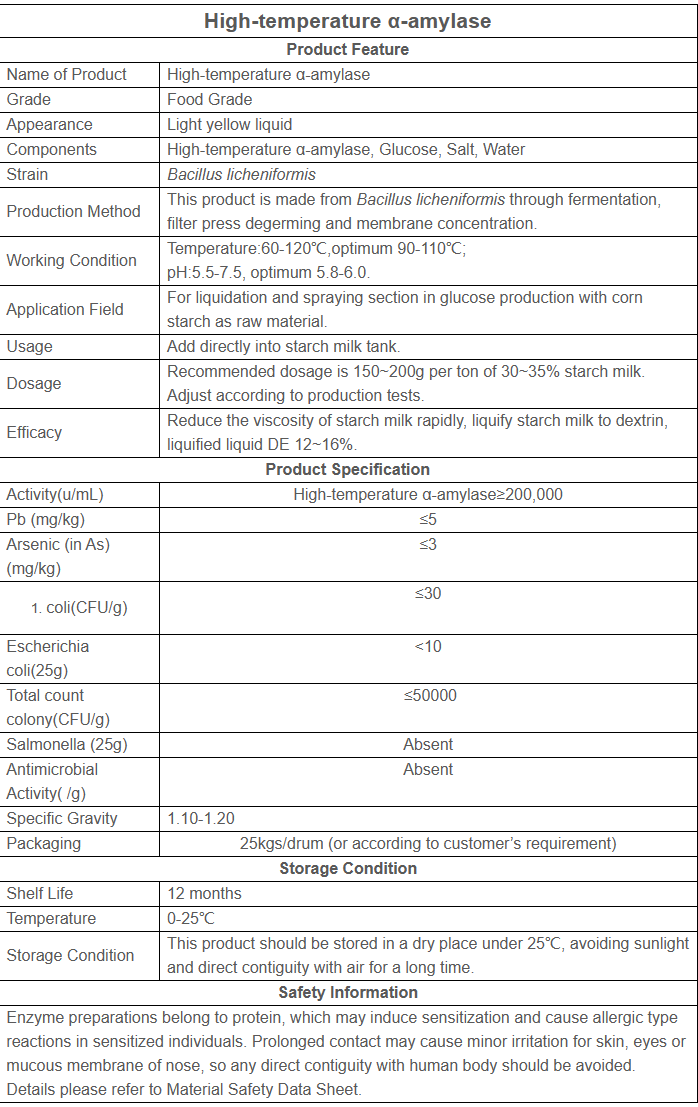
Starch sugar amylase -HTAA50L-Liquid High temperature alpha-amylase heat stable alpha amylase



Function
Alpha-amylase is an enzyme that plays a key role in a series of biochemical reactions. Here is a brief introduction to the role of α-amylase:
1.Starch Digestion: Alpha-amylase plays an important role in the digestive system. It breaks down starch into smaller polysaccharide molecules such as dextrin and maltose. This breakdown helps the body absorb and utilize the energy in starch.
2.Pasta making: In pasta making, alpha-amylase is used as a dough improver. Its function is to break down the starch molecules in flour and release the ability of starch to gelatinize. This helps improve the stickiness and strength of the dough, making pasta products (such as bread, cookies, etc.) fluffier and more elastic.
3.Brewing industry: Alpha-amylase is widely used in the brewing industry. When malt is used in the brewing process, alpha-amylase breaks down the starch into fermentable sugars, such as maltose. In this way, yeast can use these sugars to ferment to produce alcohol.
4.Food Processing: Alpha-amylase is also widely used in food processing. It improves the texture and mouthfeel of foods such as crispy bread, potato chips and cookies. In addition, in the manufacturing of biscuits and candies, it can also promote the decomposition and gelatinization of sugar, increasing the sweetness and taste of the product.
5.Detergent Manufacturing: Alpha-amylase is used to remove starch stains from clothing during the detergent manufacturing process. It degrades the starch molecules so that they dissolve in the water and are washed away.
6.Pulp and Paper Industry: Alpha-amylase is used as a desizing agent in the pulp and paper industry. It breaks down the starch in cellulosic materials, thereby helping to remove stains from the pulp and improve the quality and appearance of the paper.
Application
Alpha-amylase is a digestive enzyme that plays a vital role in the digestive system of humans and animals. It is primarily used to hydrolyze starch and other complex carbohydrates, breaking them down into simpler sugars that are easier to digest and absorb. The following are the functions and applications of α-amylase solution in different fields:
1.Food Industry: Alpha-amylase is widely used in the food industry. It can be used during flour processing to help degrade starch molecules and make dough more elastic and sticky. It also helps convert starches into sugars needed for fermentation during winemaking and brewing. In addition, α-amylase can also be used in the processing of starch products to make the products have better texture.
2.Feed industry: In animal husbandry, alpha-amylase can be added to animal feed to improve the animal's ability to digest and absorb starch. This improves feed utilization efficiency and promotes animal growth and development.
3.Biopharmaceuticals: Alpha-amylase also has applications in the biopharmaceutical field. It can be used to produce some important pharmaceutical products, such as antibiotics, vitamins and enzyme drugs. By using alpha-amylase to convert specific substrates, drug yield and purity can be improved.
4.Textile industry: In the textile industry, alpha-amylase can be used in the pretreatment process of fabrics. It breaks down starch stains on fabrics, making cleaning easier and more effective.
5.Environmental protection: α-amylase is also used in the field of environmental protection. It can be used to treat starch-containing wastewater and sludge to promote the decomposition and removal of organic matter.
Related Products:
Newgreen factory also supplies Enzymes as following:
| Food grade bromelain | Bromelain ≥ 100,000 u/g |
| Food grade alkaline protease | Alkaline protease ≥ 200,000 u/g |
| Food grade papain | Papain ≥ 100,000 u/g |
| Food grade laccase | Laccase ≥ 10,000 u/L |
| Food grade acid protease APRL type | Acid protease ≥ 150,000 u/g |
| Food grade cellobiase | Cellobiase ≥1000 u/ml |
| Food grade dextran enzyme | Dextran enzyme ≥ 25,000 u/ml |
| Food grade lipase | Lipases ≥ 100,000 u/g |
| Food grade neutral protease | Neutral protease ≥ 50,000 u/g |
| Food-grade glutamine transaminase | Glutamine transaminase≥1000 u/g |
| Food grade pectin lyase | Pectin lyase ≥600 u/ml |
| Food grade pectinase (liquid 60K) | Pectinase ≥ 60,000 u/ml |
| Food grade catalase | Catalase ≥ 400,000 u/ml |
| Food grade glucose oxidase | Glucose oxidase ≥ 10,000 u/g |
| Food grade alpha-amylase
(resistant to high temperatures) |
High temperature α-amylase ≥ 150,000 u/ml |
| Food grade alpha-amylase
(medium temperature) AAL type |
Medium temperature
alpha-amylase ≥3000 u/ml |
| Food-grade alpha-acetyllactate decarboxylase | α-acetyllactate decarboxylase ≥2000u/ml |
| Food-grade β-amylase (liquid 700,000) | β-amylase ≥ 700,000 u/ml |
| Food grade β-glucanase BGS type | β-glucanase ≥ 140,000 u/g |
| Food grade protease (endo-cut type) | Protease (cut type) ≥25u/ml |
| Food grade xylanase XYS type | Xylanase ≥ 280,000 u/g |
| Food grade xylanase (acid 60K) | Xylanase ≥ 60,000 u/g |
| Food grade glucose amylase GAL type | Saccharifying enzyme ≥ 260,000 u/ml |
| Food grade Pullulanase (liquid 2000) | Pullulanase ≥2000 u/ml |
| Food grade cellulase | CMC≥ 11,000 u/g |
factory environment

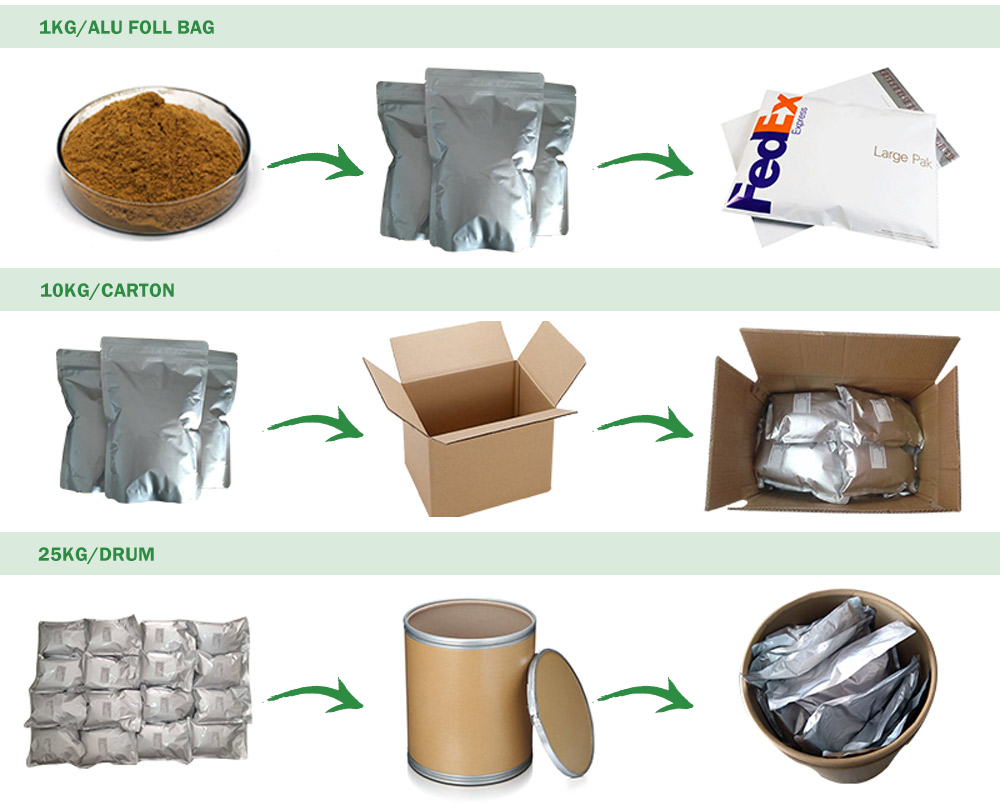
package & delivery


transportation