Researchers have discovered a potential new treatment for Alzheimer’s disease in the form of EGCG, a compound found in green tea. A study published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry found that EGCG can disrupt the formation of amyloid plaques, which are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. The researchers conducted experiments on mice and found that EGCG reduced the production of amyloid beta proteins, which are known to accumulate and form plaques in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients. This finding suggests that EGCG could be a promising candidate for the development of new therapies for Alzheimer’s disease.

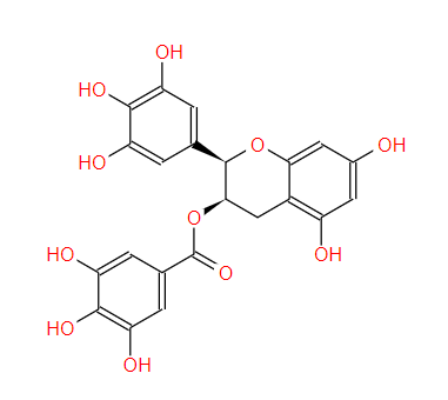
The Science Behind EGCG: Exploring its Health Benefits and Potential Applications :
The study also found that EGCG can help to protect brain cells from the toxic effects of amyloid beta proteins. This is significant because the death of brain cells is a major factor in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. By preventing the toxic effects of amyloid beta proteins, EGCG could potentially slow down the progression of the disease and preserve cognitive function in patients.
In addition to its potential benefits for Alzheimer’s disease, EGCG has also been studied for its anti-cancer properties. Research has shown that EGCG can inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in cancer cells. This suggests that EGCG could be a valuable tool in the development of new cancer treatments.
Furthermore, EGCG has been found to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which could make it beneficial for a range of health conditions. Studies have shown that EGCG can help to reduce inflammation in the body and protect cells from oxidative damage. This could have implications for conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis.

The discovery of EGCG’s potential benefits for Alzheimer’s disease and its known anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties make it an exciting area of research. Further studies will be needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action of EGCG and to determine its potential as a therapeutic agent for various health conditions. However, the findings so far suggest that EGCG could hold promise for the development of new treatments for Alzheimer’s disease and other health conditions.
Post time: Jul-29-2024