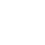
Research shows that approximately 537 million adults worldwide have type 2 diabetes, and that number is rising. The high blood sugar levels caused by diabetes can lead to a host of dangerous conditions, including heart disease, vision loss, kidney failure, and other major health problems. All of which can greatly accelerate aging.
Tetrahydrocurcumin, derived from turmeric root, has been shown in clinical studies to help reduce multiple risk factors for type 2 diabetes and lower blood sugar in people with diabetes or prediabetes. Treating type 2 diabetes can be challenging for both patients and doctors. While doctors typically recommend diet, exercise, and medication to treat people with type 2 diabetes, research suggests that tetrahydrocurcumin can provide additional support.
• Insulin Resistance And Diabetes
When we eat, our blood sugar rises. This signals the pancreas to release a hormone called insulin, which helps cells use glucose to produce energy. As a result, blood sugar drops again. Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance because cells don't respond normally to the hormone. Blood sugar levels remain elevated, a condition called hyperglycemia. High blood sugar levels can lead to systemic complications, including heart, blood vessel, kidney, eye, and nervous system disorders, and increase the risk of cancer.
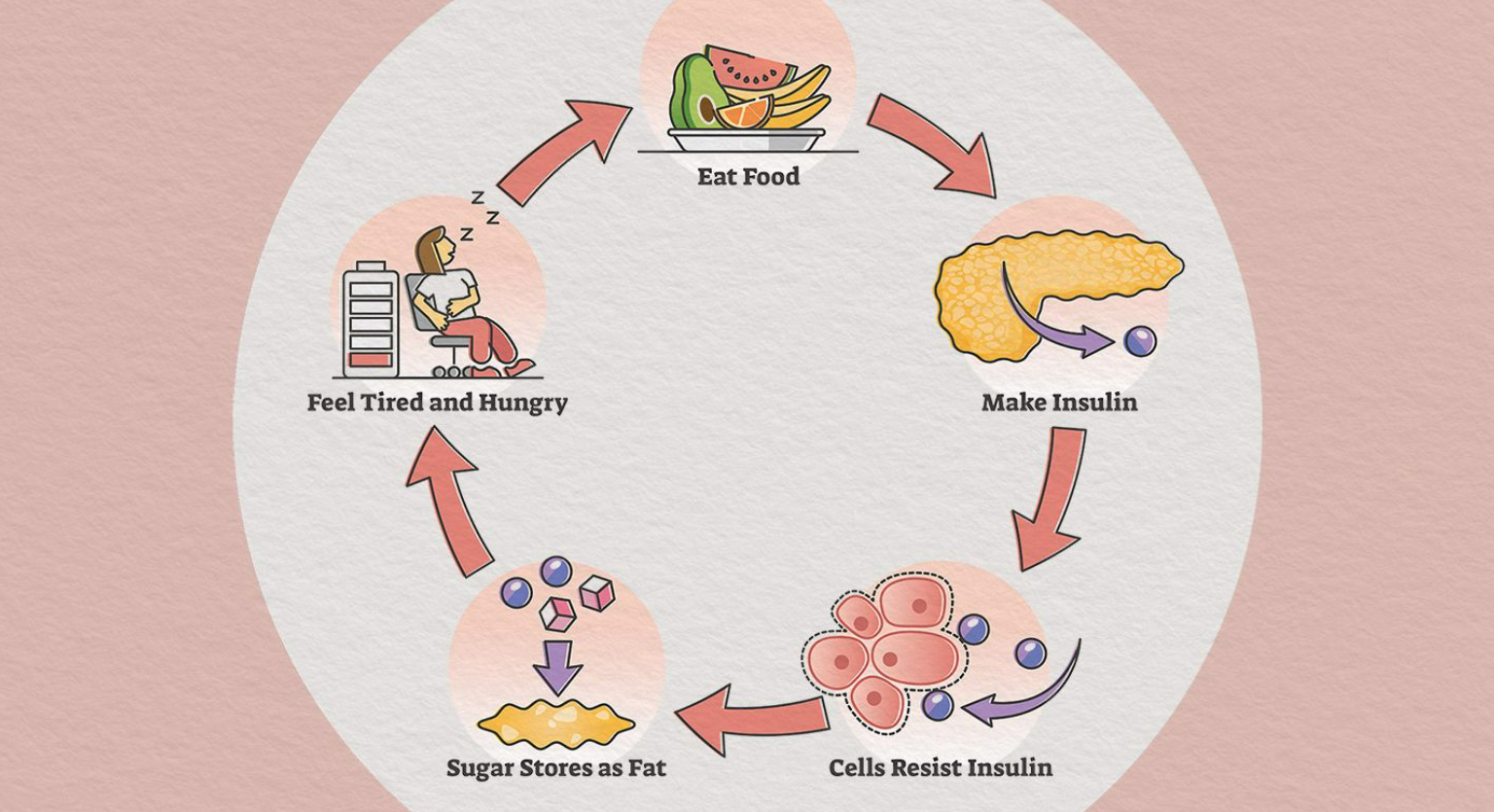
Inflammation may contribute to insulin resistance and worsen hyperglycemia in people with diabetes. [8,9] High blood sugar levels trigger more inflammation, which accelerates aging and increases the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer. Excess glucose also causes oxidative stress, which can severely damage cells and tissues. Among other problems, oxidative stress can lead to: decreased glucose transport and insulin secretion, protein and DNA damage, and increased vascular permeability.
• What Are The Benefits Of Tetrahydrocurcumin In Diabetes ?
As an active ingredient in turmeric, Tetrahydrocurcumin can help prevent the development of diabetes and the damage it can cause in a number of ways, including:
1. Activation of PPAR-γ, which is a metabolic regulator that increases insulin sensitivity and reduces insulin resistance.
2. Anti-inflammatory effects, including inhibition of signaling molecules that increase inflammation.
3. Improved function and health of insulin-secreting cell.
4. Reduced formation of advanced glycation end products and prevented the damage they cause.
5. Antioxidant activity, which reduces oxidative stress.
6. Improved lipid profiles and reduced some markers of metabolic dysfunction and heart disease.
In animal models, tetrahydrocurcumin shows promise in helping prevent the development of diabetes and reducing insulin resistance.

• What Are The Benefits Of Tetrahydrocurcumin In Cardiovascular ?
A 2012 study published in the International Journal of Pharmacology evaluated the effects of tetrahydrocurcumin on mouse aortic rings to see if the compound had cardioprotective properties. First, the researchers dilated the aortic rings with carbachol, a compound known for inducing vasodilation. Then, the mice were injected with homocysteine thiolactone (HTL) to inhibit vasodilation. [16] Finally, the researchers injected mice with either 10 μM or 30 μM of tetrahydrocurcumin and found that it induced vasodilation at levels similar to carbachol.
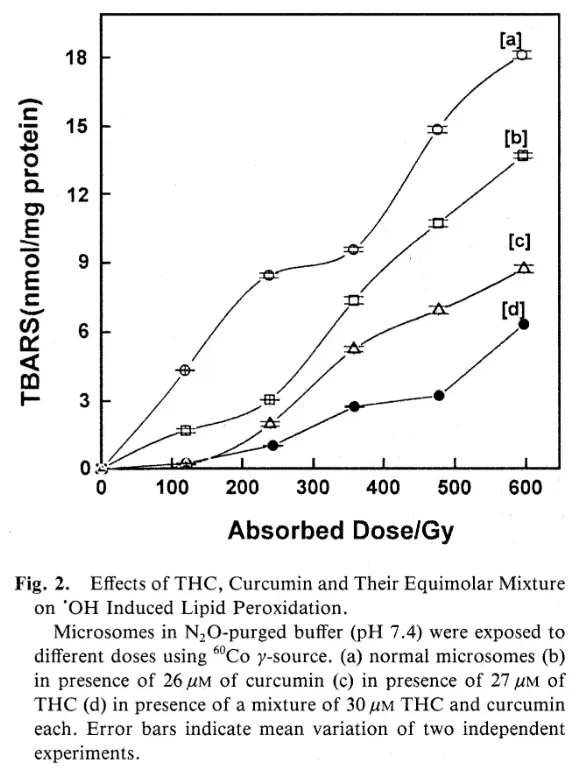
According to this study, HTL produces vasoconstriction by decreasing the amount of nitric oxide in the blood vessels and increasing the production of free radicals. Therefore, tetrahydrocurcumin must affect the production of nitric oxide and/or free radicals in order to restore vasodilation. Since tetrahydrocurcumin has strong antioxidant properties, it may be able to scavenge free radicals.
• What Are The Benefits Of Tetrahydrocurcumin In Hypertension ?
Although high blood pressure can have a variety of causes, it is usually the result of excessive constriction of blood vessels, which leads to narrowing of the blood vessels.
In a 2011 study, researchers gave tetrahydrocurcumin to mice to see how it affected blood pressure. To induce vascular dysfunction, the researchers utilized L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME). The mice were divided into three groups. The first group received L-NAME, the second group received tetrahydrocurcumin (50mg/kg body weight) and L-NAME, and the third group received tetrahydrocurcumin (100mg/kg body weight) and L-NAME.
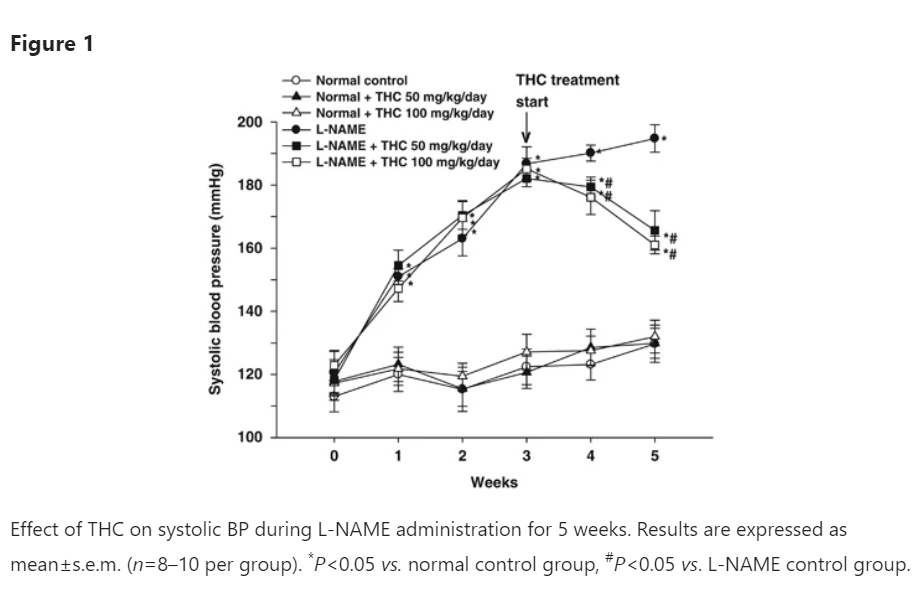
After three weeks of daily dosing, the tetrahydrocurcumin group showed a significant reduction in blood pressure compared to the group that only took L-NAME. The group that was given the higher dose had a better effect than the group that was given the lower dose. The researchers attributed the good results to tetrahydrocurcumin's ability to induce vasodilation.
Post time: Oct-10-2024