• What Is Lycopene?
Lycopene is a carotenoid found in plant foods and is also a red pigment. It is found in high concentrations in mature red plant fruits and has a strong antioxidant function. It is especially abundant in tomatoes, carrots, watermelons, papayas, and guavas. It can be used as a pigment in food processing and is also often used as a raw material for antioxidant health foods.
• Physical And Chemical Properties of Lycopene
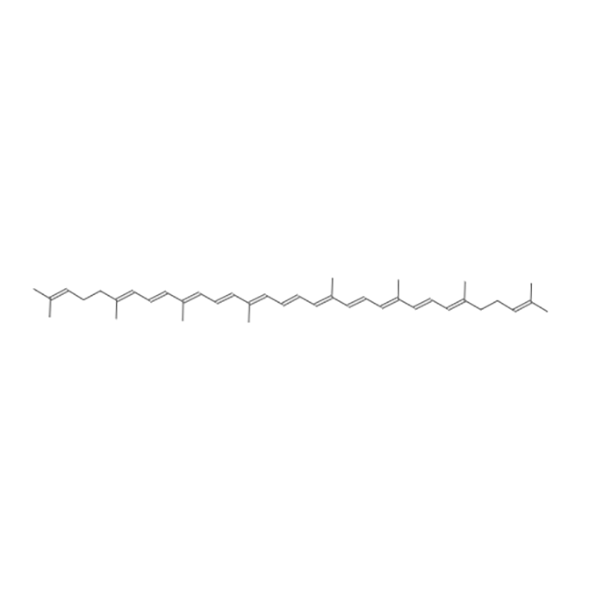
1. Chemical Structure
Chemical Name: Lycopene
Molecular Formula: C40H56
Molecular Weight: 536.87 g/mol
Structure: Lycopene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with a long chain of conjugated double bonds. It consists of 11 conjugated double bonds and 2 non-conjugated double bonds, giving it a linear structure.
2. Physical Properties
Appearance: Lycopene is typically a red to deep red crystalline powder.
Odor: It has a mild, characteristic odor.
Melting Point: Lycopene has a melting point of approximately 172-175°C (342-347°F).
Solubility:
Soluble in: Organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and hexane.
Insoluble in: Water.
Stability: Lycopene is sensitive to light, heat, and oxygen, which can cause it to degrade. It is more stable in its natural food matrix than in isolated form.
3. Chemical Properties
Antioxidant Activity: Lycopene is a potent antioxidant, capable of neutralizing free radicals and preventing oxidative damage to cells and tissues.
Isomerization: Lycopene can exist in several isomeric forms, including all-trans and various cis-isomers. The all-trans form is the most stable and predominant in fresh tomatoes, while cis-isomers are more bioavailable and are formed during processing and cooking.
Reactivity: Lycopene is relatively reactive due to its high degree of unsaturation. It can undergo oxidation and isomerization reactions, especially when exposed to light, heat, and oxygen.
4. Spectral Properties
UV-Vis Absorption: Lycopene has a strong absorption in the UV-Vis region, with a maximum absorption peak around 470-505 nm, which gives it its characteristic red color.
NMR Spectroscopy: Lycopene can be characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, which provides information about its molecular structure and the environment of its hydrogen atoms.
5. Thermal Properties
Thermal Degradation: Lycopene is sensitive to high temperatures, which can lead to its degradation and loss of antioxidant activity. It is more stable at lower temperatures and in the absence of light and oxygen.
6. Crystallography
Crystal Structure: Lycopene can form crystalline structures, which can be analyzed using X-ray crystallography to determine its precise molecular arrangement.

• What Are The Benefits Of Lycopene?
1. Antioxidant Properties
- Neutralizes Free Radicals: Lycopene is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress and damage cells.
- Prevents Oxidative Damage: By neutralizing free radicals, lycopene helps prevent oxidative damage to DNA, proteins, and lipids, which can contribute to aging and various diseases.
2. Cardiovascular Health
- Reduces LDL Cholesterol: Lycopene has been shown to reduce levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which is often referred to as "bad" cholesterol.
- Improves Blood Vessel Function: Lycopene helps improve the function of blood vessels, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
- Lowers Blood Pressure: Some studies suggest that lycopene can help lower blood pressure, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
3. Cancer Prevention
- Reduces Cancer Risk: Lycopene has been associated with a reduced risk of several types of cancer, including prostate, breast, lung, and stomach cancers.
- Inhibits Cancer Cell Growth: Lycopene can inhibit the growth and proliferation of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancerous cells.
4. Skin Health
- Protects Against UV Damage: Lycopene helps protect the skin from damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation, reducing the risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage.
- Improves Skin Texture: Regular consumption of lycopene-rich foods can improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Reduces Inflammation: Lycopene has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce skin inflammation and redness.
5. Eye Health
- Protects Against Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Lycopene helps protect the eyes from oxidative stress, reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss in older adults.
- Improves Vision: Lycopene can help maintain healthy vision by protecting the retina and other parts of the eye from oxidative damage.
6. Bone Health
- Reduces Bone Loss: Lycopene has been shown to reduce bone resorption (breakdown) and increase bone mineral density, which can help prevent osteoporosis and fractures.
- Promotes Bone Formation: Lycopene supports the formation of new bone tissue, contributing to overall bone health.
7. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
- Reduces Inflammation: Lycopene has strong anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce chronic inflammation, which is linked to various diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
- Alleviates Pain: By reducing inflammation, lycopene can also help alleviate pain associated with inflammatory conditions such as arthritis.
8. Neurological Health
- Protects Against Neurodegenerative Diseases: Lycopene's antioxidant properties help protect brain cells from oxidative damage, reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
- Improves Cognitive Function: Some studies suggest that lycopene can improve cognitive function and memory, particularly in older adults.
• What Are The Applications Of Lycopene?
1.Food and Beverage Industry
Functional Foods and Beverages
- Fortified Foods: Lycopene is added to various food products such as cereals, dairy products, and snacks to enhance their nutritional value.
- Beverages: Lycopene is used in health drinks, smoothies, and juices to provide antioxidant benefits and improve overall health.
Natural Food Colorant
- Coloring Agent: Lycopene is used as a natural red or pink colorant in foods and beverages, providing an appealing color without synthetic additives.
2. Dietary Supplements
Antioxidant Supplements
- Capsules and Tablets: Lycopene is available in supplement form, often in capsules or tablets, to provide a concentrated dose of antioxidants.
- Multivitamins: Lycopene is included in multivitamin formulations to enhance their antioxidant properties and support overall health.
Heart Health Supplements
- Cardiovascular Support: Lycopene supplements are marketed for their potential to support heart health by reducing LDL cholesterol and improving blood vessel function.
3. Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
Skincare Products
- Anti-Aging Creams: Lycopene is used in anti-aging creams and serums for its antioxidant properties, which help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Sunscreens: Lycopene is included in sunscreens and after-sun products to protect the skin from UV damage and reduce inflammation.
Hair Care Products
- Shampoos and Conditioners: Lycopene is used in hair care products to protect hair from oxidative damage and improve scalp health.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry
Therapeutic Agents
- Cancer Prevention: Lycopene is studied for its potential role in cancer prevention, particularly for prostate, breast, and lung cancers.
- Cardiovascular Health: Lycopene is investigated for its benefits in reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improving heart health.
Topical Treatments
- Wound Healing: Lycopene is used in topical formulations to promote wound healing and reduce inflammation.
5. Agriculture and Animal Feed
Animal Nutrition
- Feed Additive: Lycopene is added to animal feed to improve the health and productivity of livestock by providing antioxidant protection.
Plant Growth
- Plant Supplements: Lycopene is used in agricultural products to enhance the growth and health of plants by protecting them from oxidative stress.
6. Biotechnology and Research
Biomarker Studies
- Disease Biomarkers: Lycopene is used in research to study its potential as a biomarker for various diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Nutritional Research
- Health Benefits: Lycopene is extensively studied for its health benefits, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties.
• Food Sources of Lycopene
Mammals cannot synthesize lycopene on their own and must obtain it from vegetables and fruits. Lycopene is mainly found in foods such as tomatoes, watermelons, grapefruits and guava. The content of lycopene in tomatoes varies with the variety and maturity. The higher the maturity, the higher the lycopene content. The lycopene content in fresh ripe tomatoes is generally 31-37 mg/kg. The lycopene content in commonly consumed tomato juice/sauce is about 93-290 mg/kg depending on the concentration and production method. Other fruits with high lycopene content include guava (about 52 mg/kg), watermelon (about 45 mg/kg), grapefruit (about 14.2 mg/kg), etc. Carrots, pumpkins, plums, persimmons, peaches, mangoes, pomegranates, grapes and other fruits and vegetables can also provide a small amount of lycopene (0.1-1.5 mg/kg).
Related Questions You can Be Interested In :
♦ What are the side effects of lycopene?
Lycopene is generally considered safe for most people when consumed in amounts typically found in foods. However, like any substance, it can have side effects, especially when taken in large doses or as a supplement. Here are some potential side effects and considerations:
1. Gastrointestinal Issues
- Nausea and Vomiting: High doses of lycopene supplements can cause nausea and vomiting in some individuals.
- Diarrhea: Excessive intake may lead to diarrhea and other digestive disturbances.
- Bloating and Gas: Some people may experience bloating and gas when consuming large amounts of lycopene.
2. Allergic Reactions
- Skin Reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions such as rashes, itching, or hives.
- Respiratory Issues: In very rare cases, lycopene can cause respiratory issues like difficulty breathing or swelling of the throat.
3. Interactions with Medications
Blood Pressure Medications
- Interaction: Lycopene may interact with blood pressure medications, potentially enhancing their effects and leading to low blood pressure (hypotension).
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Drugs
- Interaction: Lycopene may have a mild blood-thinning effect, which could enhance the effects of anticoagulant and antiplatelet medications, increasing the risk of bleeding.
4. Prostate Health
- Prostate Cancer Risk: While lycopene is often studied for its potential to reduce the risk of prostate cancer, some studies suggest that extremely high levels of lycopene might have the opposite effect. However, more research is needed to confirm this.
5. Carotenodermia
- Skin Discoloration: Consuming very high amounts of lycopene can lead to a condition called carotenodermia, where the skin takes on a yellow or orange tint. This condition is harmless and reversible by reducing lycopene intake.
6. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Safety: While lycopene from food sources is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, the safety of lycopene supplements has not been well-studied. It is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before taking lycopene supplements during these periods.
7. General Considerations
Balanced Diet
- Moderation: It is important to consume lycopene as part of a balanced diet. Relying solely on supplements can lead to imbalances and potential side effects.
Consult Healthcare Providers
- Medical Advice: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
♦ Who should avoid lycopene?
While lycopene is generally safe for most people, certain individuals should exercise caution or avoid lycopene supplements. These include individuals with allergies, those taking specific medications (such as blood pressure medications and blood thinners), pregnant and breastfeeding women, individuals with prostate health concerns, people with gastrointestinal issues, and those experiencing carotenodermia. As always, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
♦ Can I take lycopene daily?
You can generally take lycopene daily, especially when it is obtained from dietary sources like tomatoes, watermelons, and pink grapefruits. Lycopene supplements can also be taken daily, but it is important to adhere to recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider, particularly if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications. Daily intake of lycopene can provide numerous health benefits, including antioxidant protection, improved cardiovascular health, reduced cancer risk, and enhanced skin health.
♦ Is lycopene safe for kidneys?
Lycopene’s antioxidant properties can help reduce oxidative stress, which is a contributing factor in the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). By neutralizing free radicals, lycopene may help protect kidney cells from damage. And Chronic inflammation is another factor that can exacerbate kidney disease. Lycopene’s anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce inflammation, potentially benefiting kidney health.
Post time: Sep-24-2024