• What Is Mandelic Acid?
Mandelic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) derived from bitter almonds. It is widely used in skincare products for its exfoliating, antibacterial, and anti-aging properties.
• Physical And Chemical Properties of Mandelic Acid
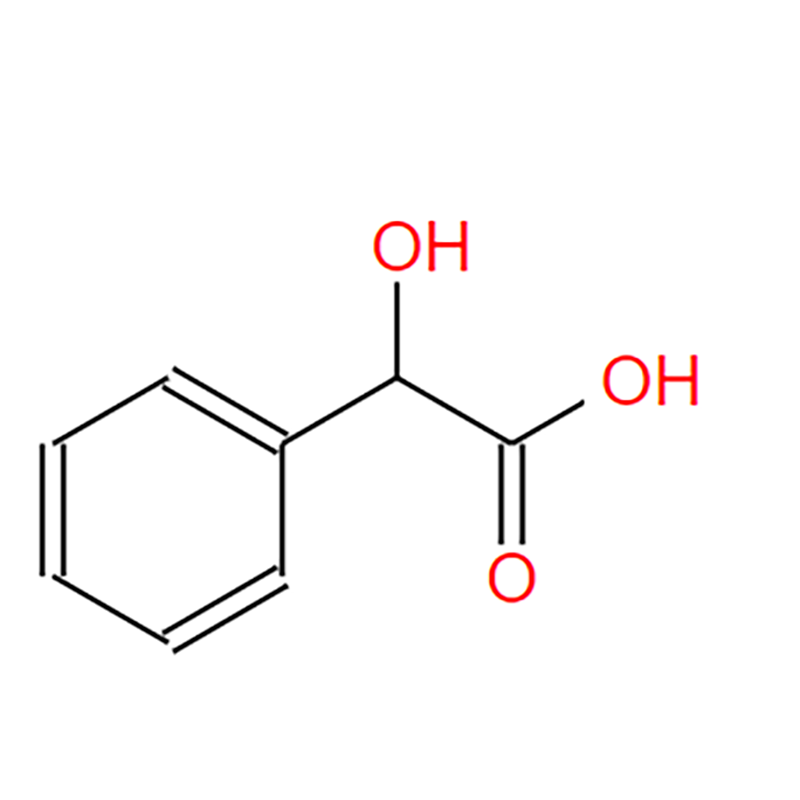
1. Chemical Structure
Chemical Name: Mandelic Acid
Molecular Formula: C8H8O3
Molecular Weight: 152.15 g/mol
Structure: Mandelic acid has a benzene ring with a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to the same carbon atom. Its IUPAC name is 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid.
2. Physical Properties
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Odor: Odorless or slightly characteristic odor
Melting Point: Approximately 119-121°C (246-250°F)
Boiling Point: Decomposes before boiling
Solubility:
Water: Soluble in water
Alcohol: Soluble in alcohol
Ether: Slightly soluble in ether
Density: Approximately 1.30 g/cm³
3.Chemical Properties
Acidity (pKa): The pKa of mandelic acid is approximately 3.41, indicating it is a weak acid.
Stability: Mandelic acid is relatively stable under normal conditions but can degrade when exposed to high temperatures or strong oxidizing agents.
Reactivity:
Oxidation: Can be oxidized to benzaldehyde and formic acid.
Reduction: Can be reduced to mandelic alcohol.
4. Spectral Properties
UV-Vis Absorption: Mandelic acid does not have significant UV-Vis absorption due to the lack of conjugated double bonds.
Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy: Characteristic absorption bands include:
O-H Stretching: Around 3200-3600 cm⁻¹
C=O Stretching: Around 1700 cm⁻¹
C-O Stretching: Around 1100-1300 cm⁻¹
NMR Spectroscopy:
¹H NMR: Shows signals corresponding to the aromatic protons and the hydroxyl and carboxyl groups.
¹³C NMR: Shows signals corresponding to the carbon atoms in the benzene ring, the carboxyl carbon, and the hydroxyl-bearing carbon.
5. Thermal Properties
Melting Point: As mentioned, mandelic acid melts at approximately 119-121°C.
Decomposition: Mandelic acid decomposes before boiling, indicating it should be handled with care at elevated temperatures.
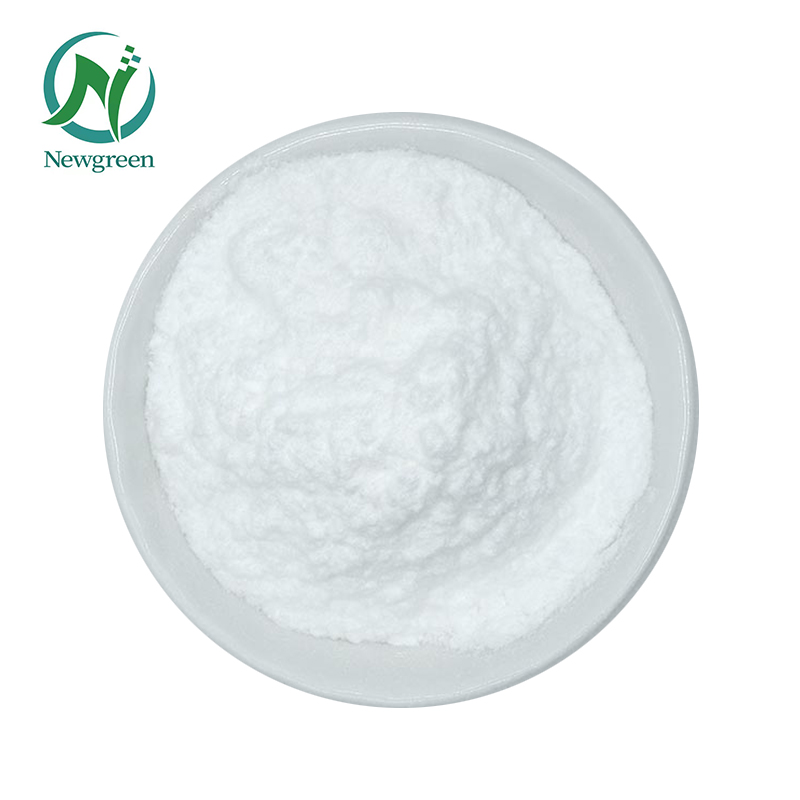

• What Are The Benefits Of Mandelic Acid?
1. Gentle Exfoliation
◊ Removes Dead Skin Cells: Mandelic acid helps to gently exfoliate the skin by breaking down the bonds between dead skin cells, promoting their removal and revealing fresher, smoother skin underneath.
◊ Suitable for Sensitive Skin: Due to its larger molecular size compared to other AHAs like glycolic acid, mandelic acid penetrates the skin more slowly, making it less irritating and suitable for sensitive skin types.
2. Anti-Aging Properties
◊ Reduces Fine Lines and Wrinkles: Regular use of mandelic acid can help reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by promoting collagen production and improving skin texture.
◊ Improves Skin Elasticity: Mandelic acid helps improve skin elasticity, making the skin appear firmer and more youthful.
3. Acne Treatment
◊ Antibacterial Properties: Mandelic acid has antibacterial properties that help reduce acne-causing bacteria on the skin, making it effective in treating and preventing acne.
◊ Reduces Inflammation: It helps reduce inflammation and redness associated with acne, promoting clearer skin.
◊ Unclogs Pores: Mandelic acid helps to unclog pores by removing dead skin cells and excess oil, reducing the occurrence of blackheads and whiteheads.
4. Hyperpigmentation and Skin Brightening
◊ Reduces Hyperpigmentation: Mandelic acid can help reduce hyperpigmentation, dark spots, and melasma by inhibiting the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color.
◊ Evens Skin Tone: Regular use can result in a more even skin tone and a brighter complexion.
5. Improves Skin Texture
◊ Smoother Skin: By promoting the removal of dead skin cells and encouraging cell turnover, mandelic acid helps to smooth out rough skin texture.
◊ Refines Pores: Mandelic acid can help to minimize the appearance of enlarged pores, giving the skin a more refined and polished look.
6. Hydration
◊ Moisture Retention: Mandelic acid helps to improve the skin’s ability to retain moisture, leading to better hydration and a plumper, more supple appearance.
7. Sun Damage Repair
◊Reduces Sun Damage: Mandelic acid can help to repair sun-damaged skin by promoting cell turnover and reducing the appearance of sunspots and other forms of hyperpigmentation caused by UV exposure.
• What Are The Applications Of Mandelic Acid?
1. Skincare Products
◊ Cleansers
Facial Cleansers: Mandelic acid is used in facial cleansers to provide gentle exfoliation and deep cleansing, helping to remove dead skin cells, excess oil, and impurities.
Toners
Exfoliating Toners: Mandelic acid is included in toners to help balance the skin’s pH, provide mild exfoliation, and prepare the skin for subsequent skincare steps.
◊ Serums
Targeted Treatments: Mandelic acid serums are popular for targeted treatment of acne, hyperpigmentation, and signs of aging. These serums deliver concentrated doses of mandelic acid to the skin for maximum efficacy.
◊ Moisturizers
Hydrating Creams: Mandelic acid is sometimes included in moisturizers to provide gentle exfoliation while hydrating the skin, improving texture and tone.
◊ Peels
Chemical Peels: Professional mandelic acid peels are used for more intensive exfoliation and skin rejuvenation. These peels help to improve skin texture, reduce hyperpigmentation, and treat acne.
2. Dermatological Treatments
◊ Acne Treatment
Topical Solutions: Mandelic acid is used in topical solutions and treatments for acne due to its antibacterial properties and ability to reduce inflammation and unclog pores.
◊ Hyperpigmentation
Brightening Agents: Mandelic acid is used in treatments for hyperpigmentation, melasma, and dark spots. It helps to inhibit melanin production and promote a more even skin tone.
◊ Anti-Aging
Anti-Aging Treatments: Mandelic acid is included in anti-aging treatments to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, improve skin elasticity, and promote collagen production.
3. Cosmetic Procedures
◊ Chemical Peels
Professional Peels: Dermatologists and skincare professionals use mandelic acid in chemical peels to provide deep exfoliation, improve skin texture, and treat various skin concerns such as acne, hyperpigmentation, and signs of aging.
◊ Microneedling
Enhanced Absorption: Mandelic acid can be used in conjunction with microneedling procedures to enhance the absorption of the acid and improve its efficacy in treating skin concerns.
4. Medical Applications
◊ Antibacterial Treatments
Topical Antibiotics: Mandelic acid’s antibacterial properties make it useful in topical treatments for bacterial skin infections and conditions.
◊ Wound Healing
Healing Agents: Mandelic acid is sometimes used in formulations designed to promote wound healing and reduce the risk of infection.
5. Hair Care Products
◊ Scalp Treatments
Exfoliating Scalp Treatments: Mandelic acid is used in scalp treatments to exfoliate dead skin cells, reduce dandruff, and promote a healthy scalp environment.
6. Oral Care Products
◊ Mouthwashes
Antibacterial Mouthwashes: Mandelic acid’s antibacterial properties make it a potential ingredient in mouthwashes designed to reduce oral bacteria and improve oral hygiene.
Related Questions You can Be Interested In :
♦ What are the side effects of mandelic acid?
While mandelic acid is generally safe and well-tolerated, it can cause side effects such as skin irritation, dryness, increased sun sensitivity, allergic reactions, and hyperpigmentation. To minimize these risks, perform a patch test, start with a lower concentration, use a hydrating moisturizer, apply sunscreen daily, and avoid over-exfoliation. If you experience persistent or severe side effects, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice.
♦ How to Use Mandelic Acid
Mandelic acid is a versatile alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that can be incorporated into your skincare routine to address various skin concerns such as acne, hyperpigmentation, and signs of aging. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to use mandelic acid effectively and safely:
1. Choosing the Right Product
Types of Products
Cleansers: Mandelic acid cleansers provide gentle exfoliation and deep cleansing. They are suitable for daily use.
Toners: Exfoliating toners with mandelic acid help balance the skin’s pH and provide mild exfoliation. They can be used daily or a few times a week, depending on your skin’s tolerance.
Serums: Mandelic acid serums offer concentrated treatment for specific skin concerns. They are typically used once or twice daily.
Moisturizers: Some moisturizers contain mandelic acid to provide hydration and gentle exfoliation.
Peels: Professional mandelic acid peels are more intensive and should be used under the guidance of a dermatologist or skincare professional.
2. Incorporating Mandelic Acid into Your Routine
Step-by-Step Guide
◊ Cleansing
Use a Gentle Cleanser: Start with a gentle, non-exfoliating cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup.
Optional: If you are using a mandelic acid cleanser, this can be your first step. Apply the cleanser to damp skin, massage gently, and rinse thoroughly.
◊ Toning
Apply Toner: If you are using a mandelic acid toner, apply it after cleansing. Soak a cotton pad with the toner and swipe it over your face, avoiding the eye area. Allow it to absorb fully before moving to the next step.
◊ Serum Application
Apply Serum: If you are using a mandelic acid serum, apply a few drops to your face and neck. Gently pat the serum into your skin, avoiding the eye area. Allow it to absorb completely.
◊ Moisturizing
Apply Moisturizer: Follow up with a hydrating moisturizer to lock in moisture and soothe the skin. If your moisturizer contains mandelic acid, it will provide additional exfoliation benefits.
◊ Sun Protection
Apply Sunscreen: Mandelic acid can increase your skin’s sensitivity to the sun. It is crucial to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every morning, even on cloudy days.
3. Frequency of Use
◊ Daily Use
Cleansers and Toners: These can be used daily, depending on your skin’s tolerance. Start with every other day and gradually increase to daily use if your skin can handle it.
Serums: Start with once daily, preferably in the evening. If your skin tolerates it well, you can increase to twice daily.
◊ Weekly Use
Peels: Professional mandelic acid peels should be used less frequently, typically once every 1-4 weeks, depending on the concentration and your skin’s tolerance. Always follow the guidance of a skincare professional.
4. Patch Testing
Patch Test: Before incorporating mandelic acid into your routine, perform a patch test to ensure you do not have an adverse reaction. Apply a small amount of the product to a discreet area, such as behind your ear or on your inner forearm, and wait 24-48 hours to check for any signs of irritation.
5. Combining with Other Skincare Ingredients
◊ Compatible Ingredients
Hyaluronic Acid: Provides hydration and pairs well with mandelic acid.
Niacinamide: Helps to soothe the skin and reduce inflammation, making it a good companion to mandelic acid.
◊ Ingredients to Avoid
Other Exfoliants: Avoid using other AHAs, BHAs (like salicylic acid), or physical exfoliants on the same day to prevent over-exfoliation and irritation.
Retinoids: Using retinoids and mandelic acid together can increase the risk of irritation. If you use both, consider alternating days or consulting a dermatologist for personalized advice.
6. Monitoring and Adjusting
◊ Observe Your Skin
Monitor Reactions: Pay attention to how your skin responds to mandelic acid. If you experience excessive redness, irritation, or dryness, reduce the frequency of use or switch to a lower concentration.
Adjust as Needed: Skincare is not one-size-fits-all. Adjust the frequency and concentration of mandelic acid based on your skin’s needs and tolerance.
Post time: Sep-24-2024