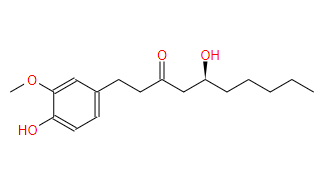
What Is Gingerol ?
Gingerol is an active ingredient extracted from the rhizome of ginger (Zingiber officinale), it is a general term for gingerrelated spicy substances, which has a strong effect against lipofuscin. Gingerol is the main pungent ingredient in ginger, giving it its unique spicy taste and aroma.
Physical And Chemical Properties of Gingerol
1.Chemical Properties
Chemical Name: Gingerol
Molecular formula: C17H26O4
Molecular Weight: 294.39 g/mol
Structural Features: Gingerol is a phenolic compound with an aromatic ring and a long alkyl side chain. Its chemical structure gives it a unique pungent taste and multiple biological activities.
Stability: Gingerol is relatively stable at room temperature, but may decompose under high temperature, strong acid or alkali conditions.
Reactivity: Gingerol has the typical reactivity of phenolic compounds and can undergo chemical reactions such as oxidation, reduction, esterification and etherification.
Antioxidant: Gingerol has powerful antioxidant properties that can neutralize free radicals and reduce the damage to cells caused by oxidative stress.
2. Physical Properties
Appearance: Gingerol is usually a yellow or light yellow crystalline solid.
Smell: Has a strong spicy taste and the unique aroma of ginger.
Melting Point: The melting point of gingerol ranges from 3032°C.
Boiling Point: The boiling point of gingerol is relatively high, usually above 300°C.
Solubility: Gingerol is soluble in ethanol, ether and other organic solvents, but insoluble in water. This necessitates the use of appropriate solvents in preparation and application of gingerol.

What Are The Benefits Of Gingerol ?
Antiinflammatory effect
1. Reduce inflammation: Gingerol has significant antiinflammatory properties, which can inhibit the production and release of inflammatory mediators and reduce inflammatory reactions.
2. Relieves Arthritis: Gingerol can effectively relieve pain and inflammation caused by arthritis and improve joint function.
Analgesic effect
1. Pain Relief: Gingerol can relieve various types of pain, especially pain associated with inflammation, such as arthritis and muscle pain.
2. Reduces Migraines: Gingerol helps relieve migraines and other types of headaches.
Antioxidant effect
1. Neutralizing Free Radicals: Gingerol has powerful antioxidant properties that can neutralize free radicals and reduce the damage to cells caused by oxidative stress.
2. Cell Protection: Through antioxidant effects, gingerol can protect cells from damage by environmental factors such as UV rays and pollution, preventing cell aging and disease.
Anticancer effect
1. Inhibit cancer cell growth: Gingerol can inhibit the growth and proliferation of various cancer cells and induce cancer cell apoptosis.
2. Antimetastatic effect: Gingerol has antimetastatic properties and can inhibit the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells.
Antibacterial and antiviral effects
1. Antibacterial effect: Gingerol has antibacterial properties and can inhibit the growth and reproduction of a variety of pathogenic bacteria.
2. Antiviral effect: Gingerol has antiviral properties, which can inhibit the activity of certain viruses and enhance the function of the immune system.
Digestive Health
1. Promote digestion: Gingerol can stimulate the secretion of gastric juice and digestive enzymes, promoting the digestion and absorption of food.
2. Relieves Nausea and Vomiting: Gingerol has antinausea and antiemetic properties and is particularly useful for relieving motion sickness, seasickness and nausea during pregnancy.
Cardiovascular Health
1. Reduce Blood Pressure: Gingerol helps lower blood pressure, improves blood circulation, and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
2. Antithrombotic: Gingerol has antithrombotic effects and helps prevent blood clots and strokes.
Immune Modulation
1. Enhance immune function: Gingerol can enhance the function of the immune system and improve the body's ability to fight infections and diseases.
2. Antiallergic effect: Gingerol has antiallergic properties, which can reduce allergic reactions and relieve allergic symptoms.
Metabolic Health
1. Regulate Blood Sugar: Gingerol helps regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and prevent and manage diabetes.
2. Promote fat metabolism: Gingerol can promote fat metabolism and help lose weight and control weight.
Skin Health
1. AntiAging: Gingerol has antiaging properties that reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles and improves skin elasticity and firmness.
2. Antiinflammatory and Repair: Gingerol can reduce the inflammatory response of the skin, promote the regeneration and repair of skin cells, and improve the overall health of the skin.
What Are The Applications Of Gingerol?
Pharmaceutical Field
1. Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Arthritis Treatment: Gingerol is used in anti-inflammatory medications to help reduce pain and inflammation caused by arthritis and improve joint function.
- Anti-inflammatory Ointment: Gingerol can be made into a topical ointment to relieve skin inflammation and muscle pain.
2. Anti-cancer drugs
- Anti-cancer treatment: Gingerol is used in anti-cancer drugs to help inhibit the growth and metastasis of cancer cells and induce apoptosis of cancer cells.
- Adjuvant therapy: Gingerol can be used as an adjuvant therapy to enhance the effect of traditional anti-cancer therapies.
3. Digestive Drugs
- Promote Digestion: Gingerol is used in digestive medicines to help promote the secretion of gastric juice and digestive enzymes and improve digestive function.
- Anti-Nausea Drugs: Gingerol is used in anti-nausea drugs, especially for relieving motion sickness, seasickness and nausea during pregnancy.
Health Care Products Field
1. Antioxidant health products
- Antioxidant: Gingerol is used in antioxidant health products to help neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress damage to cells, and prevent cell aging and disease.
2. Immune Booster
- Immune function enhancement: Gingerol is used in immune enhancers to help enhance the function of the immune system and improve the body's ability to fight infections and diseases.
3. Cardiovascular Health
- Cardiovascular health products: Gingerol is used in cardiovascular health products to help lower blood pressure, improve blood circulation, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Food and Beverage Area
1. Condiments
- Spicy Condiments: Gingerol is used in condiments to give food and beverages a unique spicy taste and aroma, adding flavor.
2. Functional Food
- Health Food: Gingerol is used in functional foods and provides a variety of health benefits such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and digestive benefits.
- Beverage Additive: Gingerol is used in beverages to provide a refreshing spicy flavor and health benefits, and is commonly found in ginger tea and functional beverages.
Cosmetics Field
1. Anti-Aging Products
- Anti-Aging Skin Care Products: Gingerol is used in anti-aging skin care products to help reduce fine lines and wrinkles and improve skin elasticity and firmness.
2. Anti-Inflammatory and Restorative Products
- Repair Skin Care Products: Gingerol is used in anti-inflammatory and repair skin care products to help reduce the inflammatory response of the skin, promote the regeneration and repair of skin cells, and improve the overall health of the skin.
3. Whitening Products
- Whitening Skin Care Products: Gingerol is used in whitening skin care products to help even out skin tone, reduce spots and dullness, and make skin brighter and glossier.
Agriculture and Animal Health
1. Plant Protection
- Natural Fungicide: Gingerol has antibacterial properties and can be used in plant protection to help inhibit the growth and reproduction of plant pathogenic bacteria.
2. Animal Health
- Animal feed additive: Gingerol can be used as an additive in animal feed to help enhance the animal's immune system and improve disease resistance.

Related Questions You can Be Interested In :
What are the side effects of gingerol?
Although gingerol is generally considered safe, it may cause side effects in some cases. The following are the potential side effects and precautions of gingerol:
1. Gastrointestinal discomfort
- Heartburn: Gingerol may cause heartburn, especially in people with hyperacidity or stomach ulcers.
- Diarrhea: High doses of gingerol may cause diarrhea.
- Stomach Pain and Bloating: Some people may experience stomach pain or bloating after ingesting gingerol.
2. Allergic Reaction
- Skin Hypersensitivity: Some people may experience allergic skin reactions to gingerol, such as rash, itching, and redness.
- Trouble breathing: A severe allergic reaction may cause difficulty breathing, throat swelling, and asthma.
3. Hemodilution
- Increased risk of bleeding: Gingerol has anti-thrombotic effects and may increase the risk of bleeding, especially in people taking anticoagulant medications (such as warfarin).
4. Hypoglycemia
- Hypoglycemia Symptoms: Gingerol may lower blood sugar levels, causing symptoms of hypoglycemia such as dizziness, fatigue, sweating, and heart palpitations.
5. Drug Interactions
- Drug Interactions: Gingerol may interact with certain medications, affecting their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. For example, gingerol may enhance the effects of anticoagulant, antidiabetic, and antihypertensive medications.
Is gingerol only found in ginger?
At present, gingerol is mainly considered to be a compound unique to ginger, and significant amounts of gingerol have not been found in other plants.
- Ginger Rhizome: Gingerol is mainly found in the rhizome of ginger and is the main pungent component of ginger. Ginger rhizome is not only rich in gingerol, but also contains other active ingredients, such as gingerol, Shogaol and Zingerone, which together give ginger its unique flavor and pharmacological effects.
- Fresh vs. Dried Ginger: Gingerol is found in both fresh and dried ginger, but the amount and form may vary. The gingerol content in fresh ginger is higher, while the gingerol in dried ginger may be partially converted into other compounds, such as shogaol , during drying and processing.
Does gingerol help digestion?
Yes, gingerol is known to have several beneficial effects on digestion. Gingerol is one of the primary active compounds found in ginger (Zingiber officinale) and is responsible for many of its medicinal properties, including its positive impact on the digestive system. Here are some ways in which gingerol helps with digestion:
1. Stimulates Digestive Enzymes
- Increased Enzyme Activity: Gingerol can stimulate the production and activity of digestive enzymes, such as amylase and lipase, which help break down carbohydrates and fats, respectively. This can improve the efficiency of digestion and nutrient absorption.
2. Promotes Gastric Motility
- Enhanced Gastric Emptying: Gingerol has been shown to promote gastric motility, which is the movement of food through the stomach and intestines. This can help prevent bloating, indigestion, and discomfort by ensuring that food moves smoothly through the digestive tract.
3. Reduces Nausea and Vomiting
- Anti-Nausea Effects: Gingerol is well-known for its anti-nausea properties. It can be particularly effective in reducing nausea and vomiting caused by motion sickness, pregnancy (morning sickness), and chemotherapy. This makes gingerol a popular natural remedy for these conditions.
4. Alleviates Gastrointestinal Discomfort
- Soothes the Stomach: Gingerol can help soothe the stomach lining and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort. It has been used traditionally to treat various digestive issues, including indigestion, gas, and bloating.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The anti-inflammatory properties of gingerol can help reduce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, which can be beneficial for conditions like gastritis and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
5. Enhances Nutrient Absorption
- Improved Absorption: By promoting the activity of digestive enzymes and enhancing gastric motility, gingerol can improve the overall efficiency of the digestive process, leading to better nutrient absorption.
6. Antimicrobial Effects
- Inhibits Pathogens: Gingerol has antimicrobial properties that can help inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria and pathogens in the digestive tract. This can contribute to a healthier gut microbiome and reduce the risk of infections.
7. Relieves Constipation
- Laxative Effect: Gingerol can have a mild laxative effect, which can help relieve constipation by promoting bowel movements and improving overall digestive health.
Post time: Sep-19-2024