What Is Coenzyme Q10?
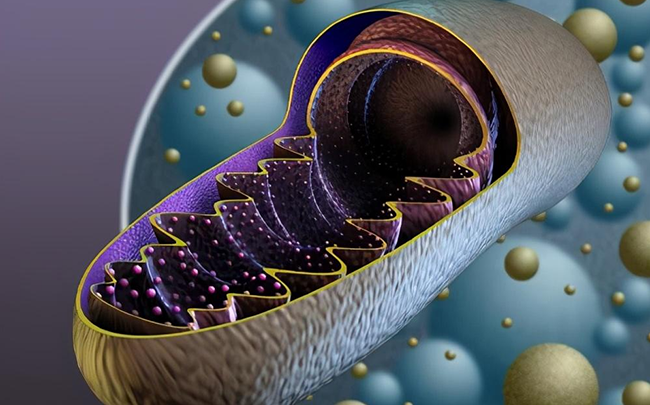
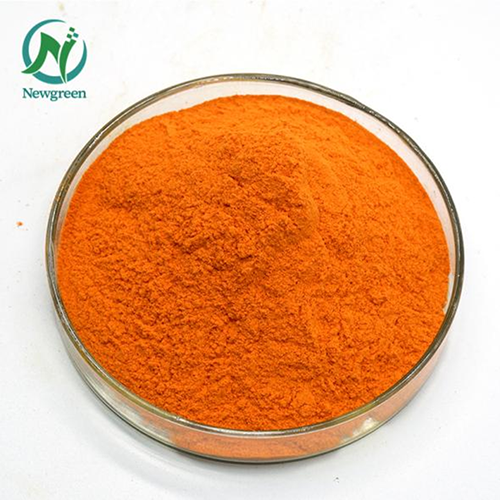
Coenzyme Q10 (Coenzyme Q10, CoQ10), also known as Ubiquinone (UQ) and Coenzyme Q (CoQ), is a coenzyme present in all eukaryotic organisms that perform aerobic respiration. It is a benzoquinone fat-soluble compound with a structure similar to vitamin K. Q represents the quinone group, and 10 represents the number of isoprene attached to its tail. It is mainly formed in the inner membrane of mitochondria, and a small part can also be obtained through food, such as beef, eggs, oily fish, nuts, oranges, broccoli and other fruits and vegetables.
Coenzyme Q10 is widely distributed in the human body and exists in various organs, tissues, subcellular components and plasma, but its content varies greatly. The mass concentration is higher in tissues and organs such as the liver, heart, kidneys and pancreas. The main function is to drive human cells to produce energy. Coenzyme Q10 is mainly involved in the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production process, regulates the cell redox environment, carries reduced electrons into the vesicle or out of the cell during the electron membrane penetration process, and participates in the formation of the proton gradient of the inner membrane and plasma membrane. It can accelerate cell renewal and stimulate cell activity, thereby greatly promoting the ability of cells to absorb nutrients. Adding coenzyme Q10 ingredients to skin care products can effectively help skin cells actively absorb other nutrients in skin care products, and has health-preserving effects such as accelerating metabolism and slowing down aging.
As a health product, coenzyme Q10 has the functions of protecting the heart, enhancing energy, and improving immunity. It is suitable for athletes, high-intensity mental workers, and the stabilization and recovery of patients with heart disease, diabetes, etc.
Physical And Chemical Properties of Coenzyme Q10
Appearance of Coenzyme Q10: Yellow or orange-yellow crystalline powder; odorless and tasteless; easily decomposed by light.
Color: light orange to dark orange
Melting point: 49-51℃
Boiling point: 715.32℃
Density: 0.9145 g/cm3
Refractive index: 1.4760
Storage conditions: Can be stored at room temperature for a short period of time, preferably at −20℃ for long-term storage
Solubility: Easily soluble in chloroform.
Sensitivity: photosensitivity
Stability: Stable, but sensitive to light or heat, incompatible with strong oxidants.

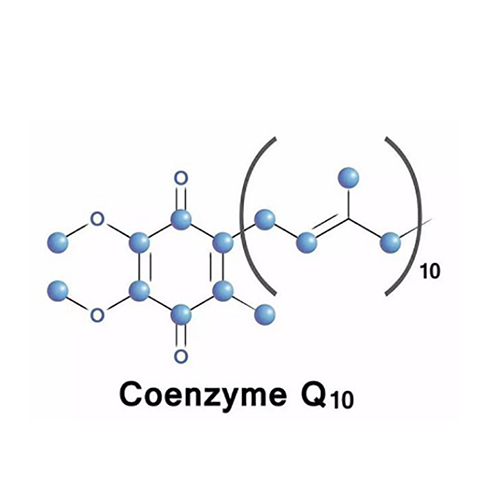
Distribution Of Coenzyme Q10 In The Human Body
Coenzyme Q10 is widely present in cell membranes, especially in mitochondrial membranes, and is mainly distributed in the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, spleen, pancreas and adrenal glands. The total body content of Coenzyme Q10 is only 500~1500mg, but it plays an important role. Coenzyme Q10 is relatively high in the heart, kidneys, liver and muscles. At the same time, 95% of Coenzyme Q10 in the human body exists in the form of ubiquinol (reduced Ubiquinol), but the brain and lungs are excluded. It is speculated that it may be due to the high oxidative stress in these two tissues, which oxidizes ubiquinol into oxidized ubiquinone (oxidized Ubiquinone).
With the decline of age, the content of Coenzyme Q10 in the human body will gradually decrease. Taking 20 years old as the standard line, at the age of 80, the natural attenuation of Coenzyme Q10 in various parts of the human body is: liver: 83.0%; kidney: 65.3%; lung: 51.7%; heart: 42.9%. Therefore, it is generally accepted that the heart is the organ that most needs coenzyme Q10 supplementation, or that many elderly heart discomforts come from a lack of coenzyme Q10.
What Are The Benefits Of Coenzyme Q10 ?
Some of the potential benefits of CoQ10 include:
1. Improved heart health: CoQ10 has been shown to support heart health by helping to improve energy production in the heart muscle, as well as acting as an antioxidant to protect against oxidative stress.
2. Increased energy production: CoQ10 is involved in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary energy source for cells. Supplementing with CoQ10 may help to increase energy levels, especially in individuals with low CoQ10 levels.
3. Antioxidant properties: CoQ10 helps to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative damage in the body, which can help to protect against various chronic diseases and support overall health.
4. Potential anti-aging effects: Some research suggests that CoQ10 may have anti-aging effects due to its ability to protect cells from oxidative damage and support cellular energy production.
5.Support for statin users: Statin medications, which are commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol, can deplete CoQ10 levels in the body. Supplementing with CoQ10 may help to mitigate the side effects of statin use, such as muscle pain and weakness.
What Is The Applications Of Coenzyme Q10 ?
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) has several applications due to its potential health benefits. Some of the key applications of CoQ10 include:
1. Heart health: CoQ10 is often used to support heart health, particularly in individuals with heart failure, high blood pressure, or other cardiovascular conditions. It may help improve energy production in the heart muscle and act as an antioxidant to protect against oxidative stress.
2. Mitochondrial disorders: CoQ10 is sometimes used as a supplement for individuals with mitochondrial disorders, as it plays a critical role in energy production within the mitochondria.
3. Statin-induced myopathy: CoQ10 supplementation is sometimes recommended for individuals taking statin medications to lower cholesterol, as statins can deplete CoQ10 levels in the body. Supplementing with CoQ10 may help alleviate muscle pain and weakness associated with statin use.
4. Anti-aging and skin health: CoQ10 is used in some skincare products due to its antioxidant properties, which can help protect the skin from oxidative damage and support overall skin health.
5. Migraine prevention: Some research suggests that CoQ10 supplementation may help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines, although more studies are needed to confirm its effectiveness for this purpose.
6. Exercise performance: CoQ10 may help improve exercise performance and recovery by supporting energy production and reducing oxidative stress in the muscles.
Coenzyme q10 Content In Common Foods
|
Coenzyme Q10 content per kg of food (mg) |
|||
|
Food |
CoQ10 content |
Food |
CoQ10 content |
|
Sardines |
33.6 |
Corn |
6.9 |
|
Saury |
26.8 |
Brown rice |
5.4 |
|
Pork heart |
25.6 |
Spinach |
5.1 |
|
Pork liver |
25.1 |
Green vegetables |
3.2 |
|
Black fish |
25.1 |
Rapeseed |
2.7 |
|
Pork loin |
24.7 |
Carrots |
2.6 |
|
Salmon |
22.5 |
Lettuce |
2.5 |
|
Mackerel |
21.8 |
Tomatoes |
2.5 |
|
Beef |
21.2 |
Kiwifruit |
2.4 |
|
Pork |
16.1 |
Celery |
2.3 |
|
Peanuts |
11.3 |
Sweet potatoes |
2.3 |
|
Broccoli |
10.8 |
Oranges |
2.3 |
|
Cherries |
10.7 |
Eggplant |
2.3 |
|
Barley |
10.6 |
Peas |
2.0 |
|
Soybeans |
7.3 |
Lotus root |
1.3 |
Related Questions You can Be Interested In :
What Are The Side Effects Of Coenzyme Q10 ?
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is generally considered safe for most people when taken in appropriate doses. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects. These can include:
1. Digestive issues: Some people may experience mild gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, or stomach upset when taking CoQ10 supplements.
2. Insomnia: In some cases, CoQ10 supplementation has been associated with difficulty sleeping or insomnia, particularly when taken in the evening.
3. Allergic reactions: Although rare, some individuals may be allergic to CoQ10 and may experience symptoms such as rash, itching, or difficulty breathing.
4. Interactions with medications: CoQ10 can interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners and medications for high blood pressure. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking CoQ10 if you are on any medications.
It's important to note that the majority of people tolerate CoQ10 well, and serious side effects are rare. However, as with any supplement, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before starting CoQ10 supplementation, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Should you take CoQ10 everyday ?
The decision to take Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) daily should be based on individual health needs and the advice of a healthcare professional. CoQ10 is naturally produced in the body and is also obtained through certain foods. However, as people age or in cases of certain health conditions, the body’s natural production of CoQ10 may decrease.
For individuals who are considering CoQ10 supplementation, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and frequency based on individual health status, potential deficiencies, and any existing medical conditions. In some cases, a healthcare professional may recommend taking CoQ10 daily, while in other situations, a different dosing schedule may be more appropriate.
Who cannot take CoQ10 ?
Certain individuals should exercise caution or avoid taking Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) without consulting a healthcare professional. These may include:
1. Pregnant or breastfeeding women: While CoQ10 is generally considered safe, there is limited research on its safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Therefore, it's advisable for pregnant or breastfeeding women to consult with a healthcare provider before using CoQ10.
2. Individuals taking blood-thinning medications: CoQ10 may interact with anticoagulant medications such as warfarin (Coumadin) or antiplatelet drugs like aspirin. It's important for individuals on these medications to seek medical advice before starting CoQ10 supplementation.
3. People with existing medical conditions: Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as liver disease, kidney disease, or diabetes, should consult with a healthcare provider before taking CoQ10, as it may interact with medications used to manage these conditions.
4. Those with known allergies: Individuals who have known allergies to CoQ10 or related compounds should avoid its use.
What are the symptoms of needing CoQ10 ?
The symptoms of needing Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) supplementation are not always straightforward, as they can be subtle and may overlap with symptoms of various health conditions. However, some potential signs that may indicate a deficiency in CoQ10 include:
1. Fatigue and low energy levels: CoQ10 plays a crucial role in the production of cellular energy. Therefore, persistent fatigue and low energy levels could potentially be a sign of CoQ10 deficiency.
2. Muscle weakness and pain: CoQ10 deficiency may contribute to muscle weakness, pain, and cramps, as it is involved in energy production within muscle cells.
3. High blood pressure: Some research suggests that low levels of CoQ10 may be associated with high blood pressure, and supplementation may help support cardiovascular health.
4. Gum disease: CoQ10 is involved in maintaining healthy gum tissue, and deficiency may contribute to gum disease or periodontal problems.
5. Migraine headaches: Some studies have indicated that CoQ10 supplementation may help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines, suggesting that low CoQ10 levels could be a contributing factor to migraines in some individuals.
How long does it take to see benefits ?
The time it takes to see the benefits of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) can vary depending on individual health status, the specific health condition being addressed, and the dosage of CoQ10 being used. In some cases, people may experience benefits relatively quickly, while in other situations, it may take longer to notice any effects.
For certain conditions such as heart failure or high blood pressure, it may take several weeks to months of consistent CoQ10 supplementation to observe improvements in symptoms. On the other hand, individuals taking CoQ10 for general energy support or as an antioxidant may notice benefits such as increased energy levels or improved overall well-being within a shorter timeframe, possibly within a few weeks.
Post time: Sep-19-2024