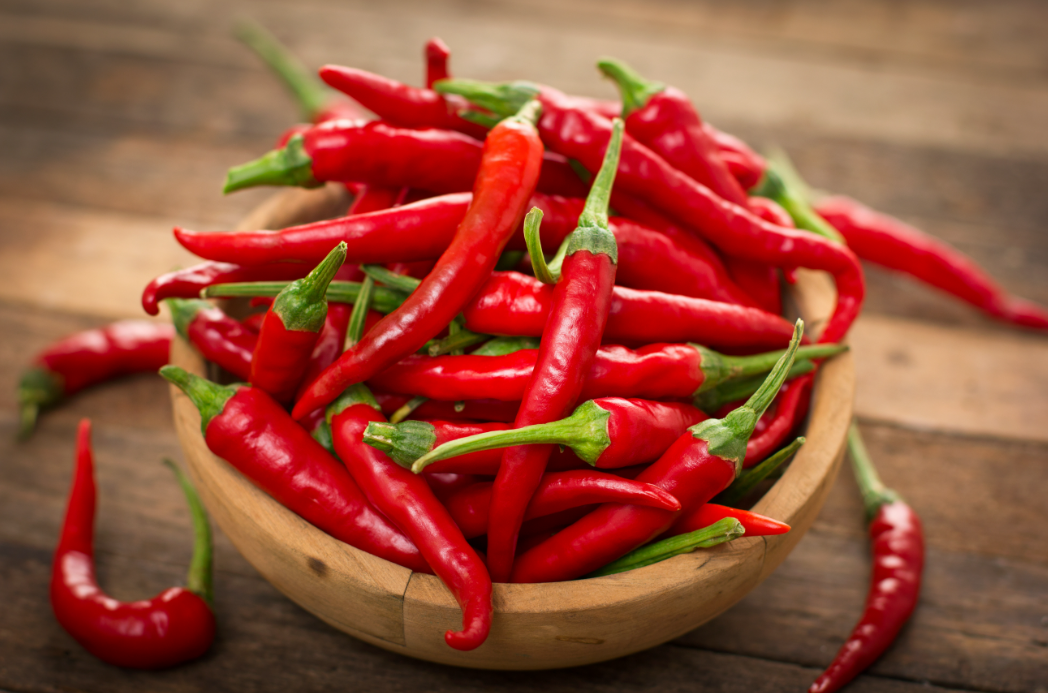
● What Is Capsaicin?
Capsaicin is a naturally occurring compound found in chili peppers that gives them their characteristic heat. It offers numerous benefits, including pain relief, metabolic and weight management, cardiovascular health, and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Capsaicin is widely used in culinary applications, medicinal products, cosmetics, and pest control.
● Physical And Chemical Properties of Capsaicin
1. Chemical Composition
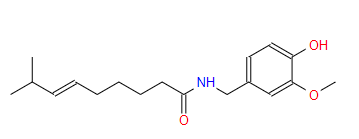
Chemical Name: 8-Methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide
Molecular Formula: C18H27NO3
Molecular Weight: 305.42 g/mol
Structure: Capsaicin is an alkaloid with a complex structure that includes a vanillyl group (a type of phenol) and a long hydrocarbon tail.
2. Physical Properties
Appearance: Capsaicin is typically a colorless, crystalline to waxy solid.
Color: Colorless to pale yellow.
Odor: Capsaicin has a pungent odor.
Taste: It is responsible for the hot, burning sensation when consumed.
Water Solubility: Slightly soluble in water (approximately 28 mg/L at 25°C).
Solubility in Other Solvents: Soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, and oils. This solubility profile makes it suitable for use in various formulations, including topical creams and culinary extracts.
Melting Point: Capsaicin has a melting point of approximately 62-65°C (144-149°F).
Boiling Point: Capsaicin decomposes before boiling, so it does not have a well-defined boiling point.
Density: The density of capsaicin is approximately 1.1 g/cm³.
3. Chemical Properties
Stability: Capsaicin is relatively stable under normal conditions but can degrade when exposed to light, heat, and air over extended periods.
Decomposition: It decomposes at high temperatures, which is why it does not have a well-defined boiling point.
pH: Capsaicin itself does not have a pH, but it can be dissolved in solutions with varying pH levels. It is generally stable in both acidic and basic environments.
Phenolic Group: The vanillyl group contains a phenolic hydroxyl group, which contributes to its reactivity and solubility in alcohols.
Amide Group: The amide linkage in capsaicin is crucial for its biological activity, particularly its interaction with the TRPV1 receptor, which is responsible for the sensation of heat and pain.
4. Biological Activity
Interaction with TRPV1 Receptor
Mechanism of Action: Capsaicin binds to the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptor, a protein found on sensory nerve endings. This interaction causes the sensation of heat and pain, which is why capsaicin is used in topical pain relief products.
Thermogenic Properties
Metabolic Effects: Capsaicin can increase thermogenesis (heat production) and energy expenditure, which is why it is often included in weight management supplements.

● Sources of Capsaicin
Capsaicin is a naturally occurring compound found in chili peppers, which belong to the genus Capsicum.
Common Varieties
Capsicum annuum: This species includes a wide range of peppers, from mild to hot, such as bell peppers, jalapeños, and cayenne peppers.
Capsicum frutescens: Includes peppers like tabasco and Thai chili peppers, known for their significant heat.
Capsicum chinense: Known for some of the hottest peppers in the world, including habaneros, Scotch bonnets, and the infamous ghost pepper (Bhut Jolokia).
Capsicum baccatum: Includes varieties like the Aji pepper, which are popular in South American cuisine.
Capsicum pubescens: Known for the rocoto pepper, which has a distinct flavor and heat level.
Capsaicinoid Content
Capsaicin and Dihydrocapsaicin: These are the most abundant capsaicinoids in chili peppers, contributing to about 80-90% of the total capsaicinoid content.
Other Capsaicinoids: Includes nordihydrocapsaicin, homocapsaicin, and homodihydrocapsaicin, which also contribute to the heat but in smaller amounts.
● What Are The Benefits Of Capsaicin ?
1. Pain Relief
Topical Analgesic
1.Mechanism: Capsaicin works by depleting substance P, a neuropeptide involved in transmitting pain signals to the brain. This makes it effective in reducing pain sensations.
2.Applications: Used in topical creams, gels, and patches to relieve pain from conditions such as arthritis, muscle strains, and neuropathy.
3.Chronic Pain Management: Effective in managing chronic pain conditions, including post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic neuropathy.
2. Metabolic and Weight Management
Thermogenesis
1.Increased Energy Expenditure: Capsaicin can increase thermogenesis (heat production) and energy expenditure, which may aid in weight management.
2.Fat Oxidation: Some studies suggest that capsaicin can enhance fat oxidation, helping the body to burn fat more efficiently.
Appetite Suppression
Reduced Calorie Intake: Capsaicin has been shown to reduce appetite and calorie intake, which can be beneficial for weight loss and weight management.
3. Cardiovascular Health
Blood Pressure Regulation
1.Vasodilation: Capsaicin promotes vasodilation (widening of blood vessels), which can help lower blood pressure.
2.Improved Circulation: Enhanced blood flow can contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
Cholesterol Levels
Lipid Profile Improvement: Some research indicates that capsaicin can help improve lipid profiles by reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol.
4. Digestive Health
Gastrointestinal Benefits
1.Stimulates Digestion: Capsaicin can stimulate the digestive tract, promoting better digestion and nutrient absorption.
2.Anti-Ulcer Properties: Contrary to popular belief, capsaicin may have protective effects against stomach ulcers by promoting the secretion of protective mucus.
5. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Oxidative Stress Reduction
Free Radical Scavenging: Capsaicin has antioxidant properties that help protect cells from oxidative stress and free radical damage, reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Inflammation Reduction
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Capsaicin exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, which can benefit conditions characterized by chronic inflammation, such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
6. Cancer Prevention
Anti-Cancer Properties
1.Apoptosis Induction: Some studies suggest that capsaicin can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, potentially inhibiting the growth of tumors.
2.Anti-Proliferative Effects: Capsaicin may also inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells, reducing the risk of cancer progression.
7. Respiratory Health
Decongestant
1.Clears Nasal Passages: Capsaicin can act as a natural decongestant, helping to clear nasal passages and relieve congestion.
2.Respiratory Benefits: It may also help in conditions like chronic rhinitis and sinusitis by reducing nasal inflammation and mucus production.
8. Skin Health
Topical Applications
1.Anti-Aging: The antioxidant properties of capsaicin can help protect the skin from oxidative stress, potentially reducing the signs of aging.
2.Skin Conditions: Capsaicin creams are sometimes used to treat skin conditions like psoriasis by reducing inflammation and pain.
● What Are The Applications Of Capsaicin?
1. Culinary Uses
◇Spice and Flavoring
Heat and Flavor: Capsaicin is responsible for the heat in chili peppers, making it a popular ingredient in many cuisines around the world, including Mexican, Indian, Thai, and Korean.
Hot Sauces and Seasonings: It is a key ingredient in hot sauces, chili powders, and spice blends, adding a spicy kick to dishes.
◇Food Preservation
Antimicrobial Properties: Capsaicin has antimicrobial properties that can help preserve food by inhibiting the growth of bacteria and fungi.
2. Medicinal Uses
◇Pain Relief
Topical Analgesics: Capsaicin is used in creams, gels, and patches to relieve pain from conditions such as arthritis, muscle strains, and neuropathy. It works by depleting substance P, a neuropeptide involved in transmitting pain signals.
Chronic Pain Management: Effective in managing chronic pain conditions, including post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic neuropathy.
◇Weight Management
Dietary Supplements: Capsaicin is included in weight management supplements for its thermogenic properties, which can increase energy expenditure and fat oxidation.
Appetite Suppression: Some supplements use capsaicin to help reduce appetite and calorie intake.
◇Cardiovascular Health
Blood Pressure Regulation: Capsaicin supplements may help lower blood pressure by promoting vasodilation (widening of blood vessels).
Cholesterol Management: Some research suggests that capsaicin can improve lipid profiles by reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol.
3. Cosmetic and Personal Care Products
◇Skin Care
Anti-Aging Products: The antioxidant properties of capsaicin can help protect the skin from oxidative stress, potentially reducing the signs of aging.
Topical Treatments: Capsaicin is used in creams and ointments to treat skin conditions like psoriasis by reducing inflammation and pain.
◇Slimming and Anti-Cellulite Products
Thermogenic Effect: Capsaicin is included in some cosmetic products aimed at reducing the appearance of cellulite and promoting slimming effects through its thermogenic properties.
4. Industrial and Agricultural Uses
◇Pest Control
Natural Pesticides: Capsaicin is used in natural pesticide formulations to deter pests without harmful chemicals. It is effective against a variety of insects and animals.
Animal Repellents: Used in products designed to repel animals such as deer, squirrels, and rodents from gardens and crops.
◇Non-Lethal Weapons
Pepper Spray: Capsaicin is the active ingredient in pepper spray, a non-lethal self-defense tool used by law enforcement and civilians to incapacitate attackers by causing intense irritation and pain.
5. Research and Development
◇Pharmaceutical Research
Drug Development: Capsaicin is studied for its potential therapeutic effects in various medical conditions, including cancer, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases.
Clinical Trials: Ongoing research aims to better understand the mechanisms of capsaicin and its potential applications in medicine.
◇Nutritional Studies
Health Benefits: Research continues to explore the health benefits of capsaicin, including its effects on metabolism, pain management, and cardiovascular health.

Related Questions You can Be Interested In :
● What Are The side effects Of Capsaicin?
While capsaicin offers numerous health benefits and has a wide range of applications, it can also cause side effects in some individuals. Here’s a detailed overview of the potential side effects and safety considerations associated with capsaicin:
1. Gastrointestinal Issues
Stomach Pain: Consuming large amounts of capsaicin can cause stomach pain and discomfort.
Nausea and Vomiting: High doses of capsaicin may lead to nausea and vomiting.
Diarrhea: Some individuals may experience diarrhea after consuming spicy foods containing capsaicin.
2. Skin and Mucous Membrane Irritation
Topical Application
Burning Sensation: Capsaicin creams and ointments can cause a burning sensation on the skin, especially when first applied.
Redness and Swelling: Some individuals may experience redness, swelling, and irritation at the site of application.
Allergic Reactions: Although rare, some people may have allergic reactions to capsaicin, resulting in itching, rash, or hives.
Contact with Eyes and Mucous Membranes
Severe Irritation: Capsaicin can cause severe irritation and a burning sensation if it comes into contact with the eyes, nose, or mouth. It is important to wash hands thoroughly after handling capsaicin products and avoid touching the face.
3. Respiratory Issues
Inhalation
Coughing and Sneezing: Inhaling capsaicin powder or fumes can cause coughing, sneezing, and throat irritation.
Breathing Difficulties: In severe cases, inhalation of capsaicin can lead to breathing difficulties and bronchospasm, particularly in individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions.
4. Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylaxis: Although extremely rare, severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis can occur, characterized by difficulty breathing, swelling of the face and throat, and a rapid drop in blood pressure. Immediate medical attention is required in such cases.
5. Potential Interactions with Medications
Blood Pressure Medications
Enhanced Effects: Capsaicin may enhance the effects of blood pressure medications, potentially leading to hypotension (low blood pressure). It is important to monitor blood pressure closely and consult a healthcare provider for appropriate dosage adjustments.
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Drugs
Increased Bleeding Risk: Capsaicin may increase the risk of bleeding when taken with anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs. Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended before using capsaicin supplements.
6. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Safety Concerns: There is limited research on the safety of capsaicin during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It is best to consult a healthcare provider before using capsaicin products if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
7. General Precautions
Consult Healthcare Providers
Medical Conditions: Individuals with underlying medical conditions, such as gastrointestinal disorders, respiratory conditions, or skin sensitivities, should consult a healthcare provider before using capsaicin products.
Start with a Low Dose: To minimize the risk of side effects, it is advisable to start with a low dose and gradually increase it as your body adjusts.
Patch Test
Allergy Test: If you are prone to allergies, consider performing a patch test before using topical capsaicin products extensively to ensure you do not have an adverse reaction.
● Who should not take capsaicin ?
While capsaicin offers numerous health benefits, it is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with allergies or sensitivities to capsaicin or chili peppers should avoid it. People with gastrointestinal disorders such as IBS, GERD, or peptic ulcers may experience aggravated symptoms. Those with respiratory conditions like asthma should avoid inhaling capsaicin. Individuals with sensitive skin or open wounds should not use topical capsaicin products. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, children, and individuals taking certain medications or with specific medical conditions should consult a healthcare provider before using capsaicin. Being aware of these considerations can help ensure the safe and effective use of capsaicin.
● What diseases does capsaicin treat?
Capsaicin is used to treat a variety of diseases and conditions, primarily due to its pain-relieving, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic effects. It is effective in managing chronic pain conditions such as arthritis, neuropathic pain, and fibromyalgia. Capsaicin is also used to relieve musculoskeletal pain from muscle strains, sprains, tendinitis, and bursitis. In dermatology, it helps manage skin conditions like psoriasis and chronic itching. Capsaicin supplements can aid in weight management and cardiovascular health by increasing thermogenesis, reducing appetite, and improving lipid profiles. It also supports digestive health and may have protective effects against stomach ulcers. In respiratory health, capsaicin acts as a natural decongestant and reduces nasal inflammation. Emerging research suggests potential anti-cancer properties, although more studies are needed. Incorporating capsaicin into treatment regimens can provide various health benefits and improve the quality of life for individuals with these conditions.
Post time: Sep-25-2024