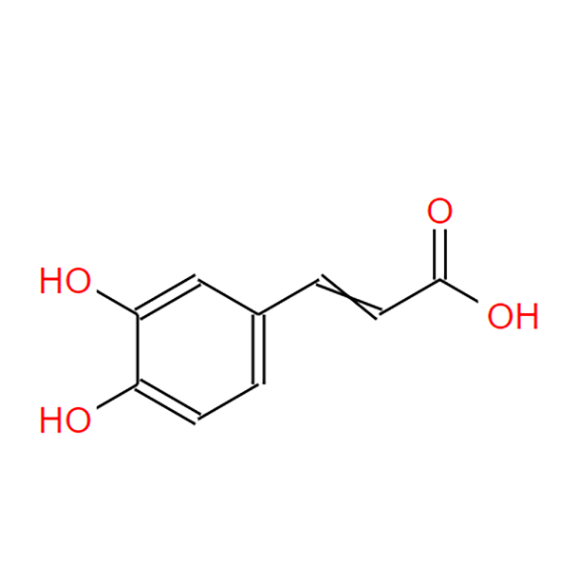
• What Is Caffeic Acid ?
Caffeic acid is a phenolic compound with significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, found in various foods and plants. Its potential health benefits and applications in food, cosmetics, and supplements make it an important compound in nutrition and health research.
Caffeic acid can be produced by plants or chemically synthesized. The following are two common methods for producing caffeic acid:
Extraction from natural sources:
Caffeic acid is found in various plants, such as coffee, apples, and artichokes. The most common way to obtain caffeic acid is to extract it from these natural sources. The extraction process involves using solvents such as methanol or ethanol to separate the caffeic acid from the rest of the plant. The extract is then purified to obtain caffeic acid.
Chemical synthesis:
Caffeic acid can also be chemically synthesized from phenol or substituted phenols. The synthesis involves reacting phenol or substituted phenols with carbon monoxide and a palladium catalyst to produce a hydroxypropyl ketone intermediate, which is then further reacted with a copper catalyst to produce caffeic acid.
This chemical synthesis method can produce caffeic acid in large quantities and can be optimized to increase the yield and purity of the product. However, the extraction method from natural sources is more environmentally friendly and produces a more natural product.
• Physical And Chemical Properties of Caffeic Acid
1. Physical Properties
Molecular Formula: C₉H₈O₄
Molecular Weight: Approximately 180.16 g/mol
Appearance: Caffeic acid typically appears as a yellowish to brown crystalline powder.
Solubility: It is soluble in water, ethanol, and methanol, but less soluble in non-polar solvents like hexane.
Melting Point: The melting point of caffeic acid is around 100-105 °C (212-221 °F).
2. Chemical Properties
Acidity: Caffeic acid is a weak acid, with a pKa value of approximately 4.5, indicating that it can donate protons in solution.
Reactivity: It can undergo various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Caffeic acid can be oxidized to form other compounds, such as quinones.
Esterification: It can react with alcohols to form esters.
Polymerization: Under certain conditions, caffeic acid can polymerize to form larger phenolic compounds.
3. Spectroscopic Properties
UV-Vis Absorption: Caffeic acid exhibits strong absorption in the UV region, which can be used for its quantification in various samples.
Infrared (IR) Spectrum: The IR spectrum shows characteristic peaks corresponding to hydroxyl (–OH) and carbonyl (C=O) functional groups.

• Extract Sources of Caffeic Acid
Caffeic acid can be extracted from various natural sources, primarily plants.
Coffee Beans:
One of the richest sources of caffeic acid, particularly in roasted coffee.
Fruits:
Apples: Contains caffeic acid in the skin and flesh.
Pears: Another fruit that has notable amounts of caffeic acid.
Berries: Such as blueberries and strawberries.
Vegetables:
Carrots: Contains caffeic acid, especially in the skin.
Potatoes: Particularly in the skin and peels.
Herbs and Spices:
Thyme: Contains significant levels of caffeic acid.
Sage: Another herb rich in caffeic acid.
Whole Grains:
Oats: Contains caffeic acid, contributing to its health benefits.
Other Sources:
Red Wine: Contains caffeic acid due to the presence of phenolic compounds in grapes.
Honey: Some varieties of honey also contain caffeic acid.
• What Are The Benefits Of Caffeic Acid ?
1. Antioxidant Properties
◊ Free Radical Scavenging: Caffeic acid helps neutralize free radicals, which can reduce oxidative stress and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects
◊ Reduction of Inflammation: It may help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to various conditions such as arthritis, heart disease, and certain cancers.
3. Potential Anti-cancer Effects
◊ Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth: Some studies suggest that caffeic acid may inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in certain types of cancer.
4. Support for Cardiovascular Health
◊ Cholesterol Management: Caffeic acid may help lower LDL cholesterol levels and improve overall heart health.
◊ Blood Pressure Regulation: It may contribute to the regulation of blood pressure, promoting better cardiovascular function.
5. Neuroprotective Effects
◊ Cognitive Health: Caffeic acid has been studied for its potential to protect against neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, by reducing oxidative stress in the brain.
6. Skin Health
◊ Anti-aging Properties: Due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, caffeic acid is often included in skincare products to help protect the skin from damage and promote a youthful appearance.
7. Digestive Health
◊ Gut Health: Caffeic acid may support gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and reducing inflammation in the digestive tract.
• What Are The Applications Of Caffeic Acid ?
Caffeic acid has a variety of applications across different fields, including food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agriculture. Here are some of the key applications:
1. Food Industry
◊ Natural Preservative: Caffeic acid is used as a natural antioxidant to extend the shelf life of food products by preventing oxidation.
◊ Flavoring Agent: It can enhance the flavor profile of certain foods and beverages, particularly in coffee and tea.
2. Pharmaceuticals
◊ Nutraceuticals: Caffeic acid is included in dietary supplements for its potential health benefits, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
◊ Therapeutic Research: It is being studied for its potential role in preventing and treating various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
3. Cosmetics and Skincare
◊ Anti-aging Products: Due to its antioxidant properties, caffeic acid is often incorporated into skincare formulations to protect the skin from oxidative damage and promote a youthful appearance.
◊ Anti-inflammatory Formulations: It is used in products aimed at reducing skin inflammation and irritation.
4. Agriculture
◊ Plant Growth Promoter: Caffeic acid can be used as a natural growth regulator to enhance plant growth and resistance to stress.
◊ Pesticide Development: Research is ongoing into its potential use as a natural pesticide due to its antimicrobial properties.
5. Research and Development
◊ Biochemical Studies: Caffeic acid is frequently used in laboratory research to study its effects on various biological processes and its potential therapeutic applications.
Related Questions You can Be Interested In :
♦ What are the side effects of caffeic acid ?
Caffeic acid is generally considered safe when consumed in moderate amounts through food sources. However, like any compound, it may have potential side effects, especially when taken in high doses or as a concentrated supplement. Here are some possible side effects:
Gastrointestinal Issues:
Some individuals may experience stomach upset, nausea, or diarrhea when consuming high amounts of caffeic acid.
Allergic Reactions:
Although rare, some people may have allergic reactions to caffeic acid or the plants that contain it, leading to symptoms like itching, rash, or swelling.
Interactions with Medications:
Caffeic acid may interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect liver enzymes. This could alter the effectiveness of the medications.
Hormonal Effects:
There is some evidence that caffeic acid may influence hormone levels, which could be a concern for individuals with hormone-sensitive conditions.
Oxidative Stress:
While caffeic acid is an antioxidant, excessive consumption may paradoxically lead to oxidative stress in some cases, particularly if it disrupts the balance of other antioxidants in the body.
♦ Is caffeic acid same as caffeine?
Caffeic acid and caffeine are not the same; they are distinct compounds with different chemical structures, properties, and functions.
KEY DIFFERENCES:
1.Chemical Structure:
Caffeic Acid: A phenolic compound with the chemical formula C9H8O4. It is a hydroxycinnamic acid.
Caffeine: A stimulant belonging to the xanthine class, with the chemical formula C8H10N4O2. It is a methylxanthine.
2.Sources:
Caffeic Acid: Found in various plants, fruits, and vegetables, particularly in coffee, fruits, and certain herbs.
Caffeine: Primarily found in coffee beans, tea leaves, cacao beans, and some soft drinks.
3.Biological Effects:
Caffeic Acid: Known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and potential health benefits, including support for cardiovascular health and skin health.
Caffeine: A central nervous system stimulant that can increase alertness, reduce fatigue, and improve concentration.
4.Uses:
Caffeic Acid: Used in food as a preservative, in cosmetics for skin health, and in research for its potential therapeutic effects.
Caffeine: Commonly consumed in beverages for its stimulating effects and is also used in some medications for pain relief and alertness.
Post time: Oct-09-2024