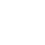
What Is Azelaic Acid ?
Azelaic Acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid that is widely used in skin care and to treat a variety of skin conditions. It has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and keratin regulating properties and is often used to treat skin problems such as acne, rosacea and hyperpigmentation.
Physical And Chemical Properties of Azelaic Acid
1. Chemical Structure and Properties
Chemical Structure
Chemical Name: Azelaic Acid
Chemical Formula: C9H16O4
Molecular Weight: 188.22 g/mol
Structure: Azelaic acid is a straight-chain saturated dicarboxylic acid.
2.Physical Properties
Appearance: Azelaic acid typically appears as a white crystalline powder.
Solubility: It is slightly soluble in water but more soluble in organic solvents like ethanol and propylene glycol.
Melting Point: Approximately 106-108°C (223-226°F).
3. Mechanism of Action
Antibacterial: Azelaic acid inhibits the growth of bacteria, particularly Propionibacterium acnes, which is a key contributor to acne.
Anti-Inflammatory: It reduces inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Keratinization Regulation: Azelaic acid helps normalize the shedding of dead skin cells, preventing clogged pores and the formation of comedones.
Tyrosinase Inhibition: It inhibits the enzyme tyrosinase, which is involved in melanin production, thereby helping to reduce hyperpigmentation and melasma.
What Are The Benefits Of Azelaic Acid?
Azelaic Acid is a versatile dicarboxylic acid widely used in skin care and treatment of a variety of skin problems. Here are the main benefits of azelaic acid:
1. Treat Acne
- Antibacterial effect: Azelaic acid can effectively inhibit the growth of Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus aureus, which are the main pathogenic bacteria of acne.
- Anti-inflammatory effect: It can reduce the inflammatory response of the skin and relieve redness, swelling and pain.
- Keratin Regulating: Azelaic acid helps normalize the shedding of dead skin cells, preventing clogged pores and acne formation.
2. Treatment of Rosacea
- Reduce Redness: Azelaic acid effectively reduces the redness and inflammation associated with rosacea.
- Antibacterial Effect: It inhibits the growth of rosacea-related bacteria and reduces the risk of skin infection.
3. Improve pigmentation
- Whitening effect: Azelaic acid helps reduce pigmentation and chloasma by inhibiting the activity of tyrosinase and reducing melanin production.
- Even Skin Tone: Regular use results in a more even skin tone, reducing dark spots and uneven pigmentation.
4. Antioxidant effect
- Neutralizing Free Radicals: Azelaic acid has antioxidant properties that neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress damage to the skin.
- Anti-Aging: By reducing free radical damage, Azelaic acid helps slow skin aging and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
5. Treatment of Post-Inflammatory Pigmentation (PIH)
- Reduce Pigmentation: Azelaic acid effectively treats post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which often occurs after acne or other inflammatory skin conditions.
- Promote skin repair: It promotes the regeneration and repair of skin cells and accelerates the fading of pigmentation.
6. Suitable for sensitive skin
- Gentle and non-irritating: Azelaic acid is generally well tolerated and suitable for sensitive skin types.
- Noncomedogenic: It does not clog pores and is suitable for acne-prone skin.
7. Treat other skin diseases
- Keratosis Pilaris: Azelaic acid can help reduce the rough, raised skin associated with Keratosis Pilaris.
- Other inflammatory skin diseases: It also has certain therapeutic effects on other inflammatory skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis.

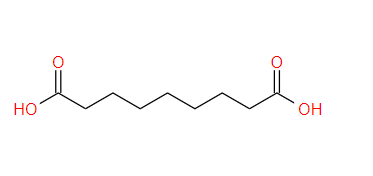
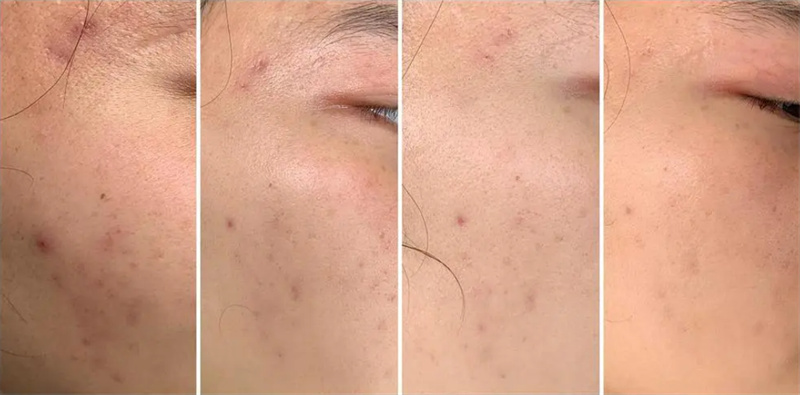
What Are The Applications Of Azelaic Acid?
1. Treat Acne: Topical preparations
- Acne Creams and Gels: Azelaic acid is commonly used in topical preparations to treat mild to moderate acne. It helps reduce the number of acne lesions and prevents the formation of new ones.
- Combination Therapy: Often used in conjunction with other acne treatments such as benzoyl peroxide or retinoic acid to enhance effectiveness.
2. Treatment of Rosacea: Anti-inflammatory preparations
- Rosacea Creams and Gels: Azelaic acid effectively reduces the redness and inflammation associated with rosacea and is often used in topical preparations specifically targeted at rosacea.
- Long-Term Management: Suitable for long-term management of rosacea, helping to maintain the stable state of the skin.
3. Improve pigmentation: Whitening Products
- Brightening Creams and Serums: Azelaic acid helps reduce pigmentation and melasma by inhibiting tyrosinase activity and reducing melanin production.
- Even Skin Tone: Regular use results in a more even skin tone, reducing dark spots and uneven pigmentation.
4. Antioxidant and anti-aging: Antioxidant skin care products
- Anti-Aging Creams and Serums: The antioxidant properties of Azelaic acid make it an important ingredient in anti-aging skin care products, helping to reduce free radical damage to the skin and slow down skin aging.
- Daily Skin Care: Suitable for daily skin care, providing antioxidant protection and keeping skin healthy.
5. Treatment of Post-Inflammatory Pigmentation (PIH): Pigmentation Repair Products
- Repair Creams and Serums: Azelaic acid is effective in treating post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and is often used in repair creams and serums to help accelerate the loss of hyperpigmentation.
- Skin Repair: Promote the regeneration and repair of skin cells and accelerate the fading of pigmentation.
6. Treat other skin diseases
Keratosis pilaris
- keratin conditioning products: Azelaic acid can help reduce the rough, raised skin associated with keratosis pilaris and is often used in keratin conditioning products.
- Skin Smoothing: Promotes skin smoothness and softness, improving skin texture.
Other inflammatory skin diseases
- Eczema and Psoriasis: Azelaic acid also has certain therapeutic effects on other inflammatory skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis, and is often used in related topical preparations.
7. Scalp Care: Anti-Inflammatory and Antibacterial Products
- Scalp Care Products: Azelaic acid’s anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties make it suitable for use in scalp care products to help reduce scalp inflammation and infection.
- Scalp Health: Promotes scalp health and reduces dandruff and itching.

Related Questions You can Be Interested In :
Does azelaic acid have side effects?
Azelaic acid can have side effects, although it is generally well-tolerated by most people. The side effects are usually mild and tend to diminish with continued use. Here are some potential side effects and considerations:
1. Common Side Effects
Skin Irritation
- Symptoms: Mild irritation, redness, itching, or a burning sensation at the application site.
- Management: These symptoms often subside as your skin adjusts to the treatment. If irritation persists, you may need to reduce the frequency of application or consult a healthcare provider.
Dryness and Peeling
- Symptoms: Dryness, flaking, or peeling of the skin.
- Management: Use a gentle moisturizer to alleviate dryness and maintain skin hydration.
2. Less Common Side Effects
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Symptoms: Severe itching, rash, swelling, or hives.
- Management: Discontinue use immediately and consult a healthcare provider if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction.
Increased Sun Sensitivity
- Symptoms: Increased sensitivity to sunlight, leading to sunburn or sun damage.
- Management: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily and avoid prolonged sun exposure.
3. Rare Side Effects
Severe Skin Reactions
- Symptoms: Severe redness, blistering, or severe peeling.
- Management: Discontinue use and seek medical advice if you experience any severe skin reactions.
4. Precautions and Considerations
Patch Test
- Recommendation: Before using azelaic acid, perform a patch test on a small area of skin to check for any adverse reactions.
Gradual Introduction
- Recommendation: If you are new to azelaic acid, start with a lower concentration and gradually increase the frequency of application to allow your skin to adjust.
Consultation
- Recommendation: Consult a dermatologist or healthcare provider before starting azelaic acid, especially if you have sensitive skin or are using other active skincare ingredients.
5. Special Populations
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
- Safety: Azelaic acid is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it is always best to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
Sensitive Skin
- Consideration: Individuals with sensitive skin should use azelaic acid with caution and may benefit from formulations designed for sensitive skin.
How long does it take to see results of azelaic acid?
The time it takes to see results from azelaic acid can vary, but initial improvements are often seen within 2 to 4 weeks for acne, 4 to 6 weeks for rosacea, and 4 to 8 weeks for hyperpigmentation and melasma. More significant results typically occur after 8 to 12 weeks of consistent use. Factors such as the concentration of azelaic acid, frequency of application, individual skin characteristics, and the severity of the condition being treated can influence the effectiveness and speed of results. Regular and consistent use, along with complementary skincare practices, can help achieve the best outcomes.
Factors Influencing Results
Concentration of Azelaic Acid
Higher Concentrations: Products with higher concentrations of azelaic acid (e.g., 15% to 20%) may produce faster and more noticeable results.
Lower Concentrations: Products with lower concentrations may take longer to show visible effects.
Frequency of Application
Consistent Use: Applying azelaic acid as directed, usually once or twice daily, can enhance the effectiveness and speed up the results.
Inconsistent Use: Irregular application may delay the visible effects and reduce overall efficacy.
Individual Skin Characteristics
Skin Type: Individual skin type and condition can influence how quickly results are seen. For example, individuals with lighter skin tones may notice results more quickly compared to those with darker skin tones.
Severity of Condition: The severity of the skin condition being treated can also affect the time it takes to see results. Mild conditions may respond faster than more severe cases.
When to use azelaic acid, morning or night?
Azelaic acid can be used both in the morning and at night, depending on your skincare routine and specific needs. If used in the morning, always follow with sunscreen to protect your skin from UV damage. Using it at night can enhance skin repair and minimize interactions with other active ingredients. For maximum benefits, some people choose to use azelaic acid both morning and night, but it’s essential to monitor your skin’s response and adjust accordingly. Always apply azelaic acid after cleansing and before moisturizing, and consider how it fits into your overall skincare regimen to achieve the best results.
What not to mix with azelaic acid ?
Azelaic acid is a versatile and generally well-tolerated skincare ingredient, but it’s important to be mindful of how it interacts with other active ingredients in your skincare routine. Mixing certain ingredients can lead to irritation, reduced efficacy, or other unwanted effects. Here are some guidelines on what not to mix with azelaic acid:
1. Strong Exfoliants
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs)
- Examples: Glycolic acid, lactic acid, mandelic acid.
- Reason: Combining azelaic acid with strong AHAs can increase the risk of irritation, redness, and peeling. Both are exfoliants, and using them together can be too harsh for the skin.
Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs)
- Examples: Salicylic acid.
- Reason: Similar to AHAs, BHAs are also exfoliants. Using them in conjunction with azelaic acid can lead to over-exfoliation and skin sensitivity.
2. Retinoids
- Examples: Retinol, Retinaldehyde, Tretinoin, Adapalene.
- Reason: Retinoids are potent ingredients that can cause dryness, peeling, and irritation, especially when first introduced. Combining them with azelaic acid can exacerbate these side effects.
3. Benzoyl Peroxide
Reason
- Irritation: Benzoyl peroxide is a strong acne-fighting ingredient that can cause dryness and irritation. Using it alongside azelaic acid can increase the risk of skin irritation.
- Reduced Efficacy: Benzoyl peroxide can also oxidize other active ingredients, potentially reducing their effectiveness.
4. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Reason
- pH Levels: Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) requires a low pH to be effective, while azelaic acid works best at a slightly higher pH. Using them together can compromise the efficacy of both ingredients.
- Irritation: Combining these two potent ingredients can increase the risk of irritation, especially for sensitive skin.
5. Niacinamide
Reason
- Potential Interaction: While niacinamide is generally well-tolerated and can be used with many active ingredients, some people may experience irritation when combining it with azelaic acid. This is not a universal rule, but it's something to be aware of.
6. Other Potent Actives
Examples
- Hydroquinone, Kojic Acid, and other skin-lightening agents.
- Reason: Combining multiple potent actives aimed at treating hyperpigmentation can increase the risk of irritation and may not necessarily enhance efficacy.
How to Incorporate Azelaic Acid Safely:
Alternate Use
- Strategy: If you want to use azelaic acid alongside other potent actives, consider alternating their use. For example, use azelaic acid in the morning and retinoids or AHAs/BHAs at night.
Patch Test
- Recommendation: Always perform a patch test when introducing a new active ingredient to your routine to check for any adverse reactions.
Start Slowly
- Strategy: Introduce azelaic acid gradually, starting with a lower concentration and increasing frequency as your skin builds tolerance.
Consult a Dermatologist
- Recommendation: If you are unsure about how to incorporate azelaic acid into your routine, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice.
Post time: Sep-21-2024