• What Is Crocin ?
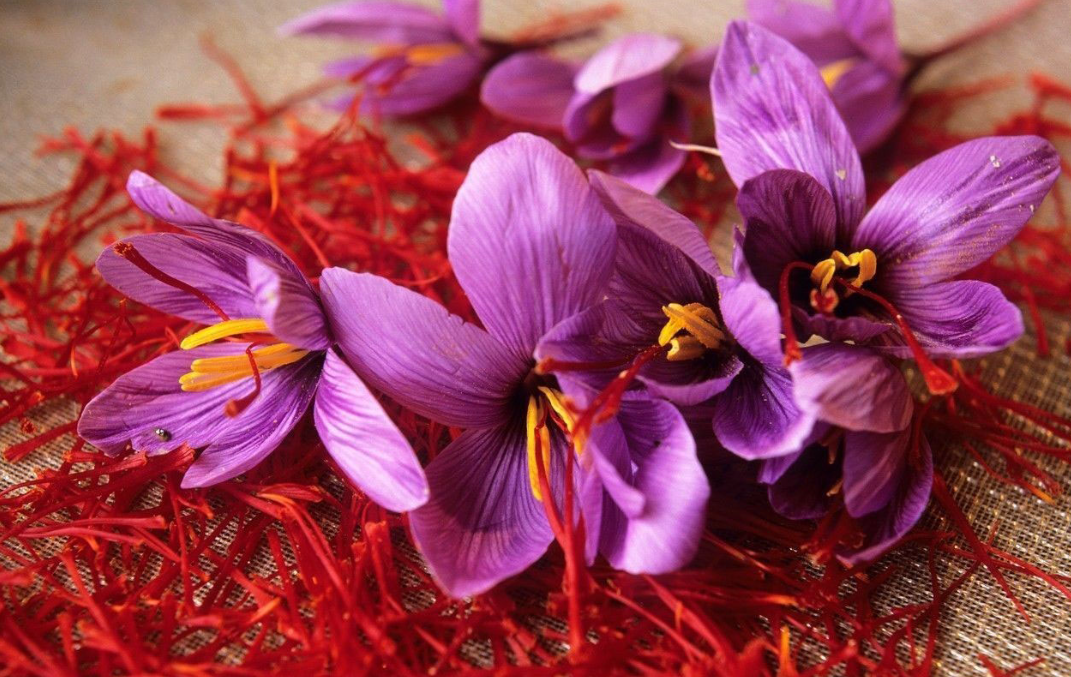
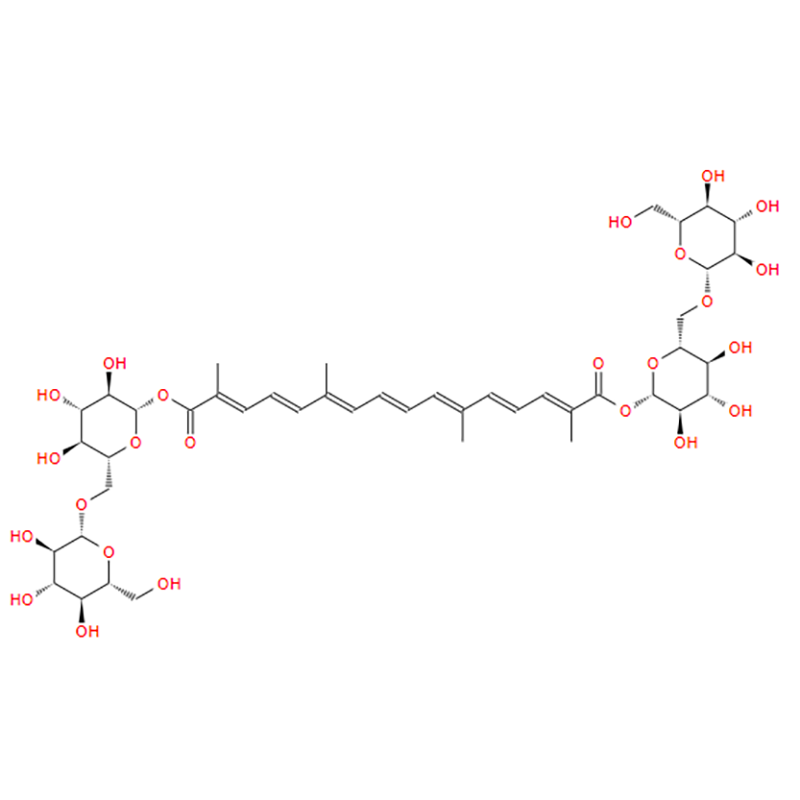
Crocin is the colored component and main component of saffron. Crocin is a series of ester compounds formed by crocetin and gentiobiose or glucose, mainly composed of crocin I, crocin II, crocin III, crocin IV and crocin V, etc. Their structures are relatively similar, and the only difference is the type and number of sugar groups in the molecule.. It is an uncommon water-soluble carotenoid (dicarboxylic acid polyene monosaccharide ester).
The distribution of crocin in the plant kingdom is relatively limited. It is mainly distributed in plants such as Crocus saffron of Iridaceae, Gardenia jasminoides of Rubiaceae, Buddleja buddleja of Loganaceae, Night-blooming cereus of Oleaceae, Burdock of Asteraceae, Stemona sempervivum of Stemonaceae and Mimosa pudica of Leguminosae. Crocin is distributed in the flowers, fruits, stigmas, leaves and roots of plants, but the content varies greatly in different plants and different parts of the same plant. For example, crocin in saffron is mainly distributed in the stigma, and crocin in Gardenia is mainly distributed in the pulp, while the content in the peel and seeds is relatively low.
• What Are The Health Benefits of Crocin ?
The pharmacological effects of crocin on the human body mainly include the following aspects:
1. Antioxidant: Crocin has the effect of scavenging free radicals and can significantly inhibit the damage of vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells induced by hydrogen peroxide.
2. Anti-aging: Crocin has the effect of delaying aging, can significantly increase SOD activity, and reduce the production of lipid peroxides.
3. Lower blood lipids: Crocin has a significant effect on lowering blood lipids and can effectively reduce the levels of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood.
4. Anti-platelet aggregation: Crocin can significantly inhibit platelet aggregation and effectively prevent thrombosis.

• What Are The Applications of Crocin ?
Application of crocin in Tibetan medicine
Crocin is not a medicine, but it is widely used in Tibetan medicine. Crocin can be used to treat a variety of diseases, such as coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, cerebral thrombosis and other diseases. Tibetan medicine believes that crocin is one of the important drugs for treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
In Tibetan medicine in China, the main applications of crocin are: used to treat cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, etc.; used to treat cerebrovascular diseases, such as cerebral thrombosis, cerebral embolism, etc.; used to treat stomach and duodenum Intestinal ulcer disease; used to treat neurasthenia, headache, insomnia, depression, etc.; used to treat skin diseases, such as neurodermatitis, etc.; used to treat colds and other symptoms.
Effect of crocin on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
Crocin has the effect of reducing blood viscosity and platelet aggregation, inhibiting excessive platelet aggregation and preventing thrombosis. Crocin can also increase the oxygen supply to myocardial cells, reduce heart rate, increase cardiac output, increase myocardial contractility, and improve myocardial oxygen supply.
Crocin can promote blood circulation in the coronary arteries and increase the oxygen and blood supply to the heart and brain tissue. Crocin can reduce blood viscosity, hematocrit and platelet count, improve blood fluidity, and prevent thrombosis.
Crocin can effectively inhibit blood coagulation and has anti-thrombotic and thrombolytic effects.
• How To Preserve Crocin ?
1. Store in the dark: The optimal storage temperature of saffron is 0℃-10℃, so the packaging of saffron should be stored in the dark, and the packaging should be made of light-proof materials.
2. Sealed storage: Crocin is very sensitive to heat and easy to decompose. Therefore, sealing saffron products effectively prevents them from spoiling. At the same time, direct sunlight should also be avoided, otherwise it will affect the stability of the product.
3. Low-temperature storage: When saffron products are stored at room temperature, reactions such as photo and thermal decomposition will occur, causing the color of the product to change. Therefore, saffron products should be stored at low temperatures.
4. Store away from light: Saffron products should be kept away from direct sunlight, otherwise it will cause discoloration of the product. In addition, the influence of too high or too low temperature should be avoided, otherwise it will affect its stability.
Post time: Oct-25-2024